If you’re looking for a new TV or monitor, you might have come across the term HDR, which stands for High Dynamic Range.
But what does it mean, and how does it compare to the standard SDR (Standard Dynamic Range) format?
In this article, we’ll explain the concept of HDR, how it enhances the picture quality, and what are the key aspects to consider when choosing between HDR and SDR.
What Is HDR and How Does It Work?
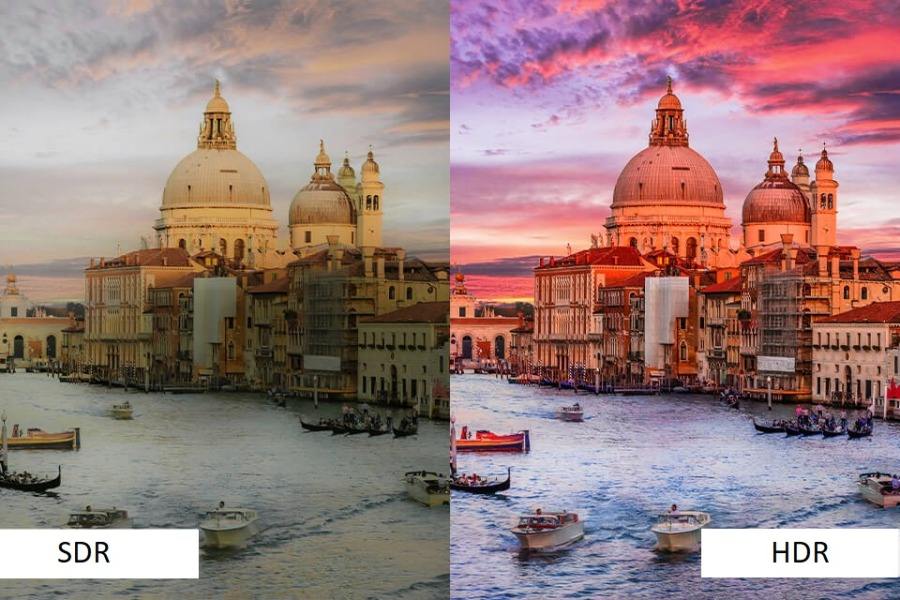
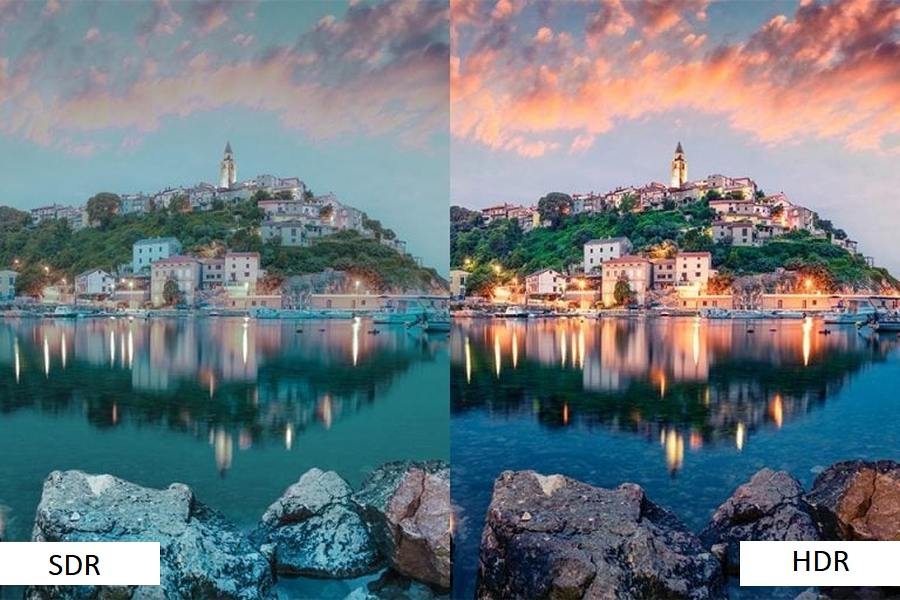
HDR is a video standard that has a wider range of colors and brightness levels than SDR. It means that HDR content can display more realistic and vivid images, with brighter highlights, deeper shadows, and more details in both dark and bright areas.
HDR also supports more color shades and hues, which results in smoother color transitions and less banding artifacts.
HDR works by sending metadata to your TV or monitor, which is a list of instructions on how to display the content properly.
The metadata tells the device what exact color and brightness level to use for each pixel, whereas SDR uses a fixed range of values.
For example, with SDR, a pixel can only have a brightness level between 0 and 100 nits, while with HDR, it can go up to 10,000 nits or more, depending on the device’s capabilities.
There are different types of HDR formats, such as HDR10, HDR10+, Dolby Vision, and HLG, and they differ in the way they use metadata.
Some formats use static metadata, which means the metadata is the same for the whole content, while others use dynamic metadata, which means the metadata can change on a scene-by-scene or even frame-by-frame basis.
Dynamic metadata allows for more accurate and optimized HDR performance, as it can adjust the brightness and color levels according to the content.
HDR vs SDR: A Comparison of Key Aspects
To better understand the difference between HDR and SDR, let’s compare some of the key aspects that affect the picture quality, such as peak brightness, color gamut, color depth, and gradient handling.
Peak Brightness
Peak brightness is the maximum brightness level that a device can produce.
It’s measured in nits, which is a unit of luminance.
The higher the peak brightness, the brighter the image and the more contrast it can create.
SDR content is mastered at a peak brightness of 100 nits, which is the standard for most TVs and monitors.
HDR content, on the other hand, is mastered at a minimum of 400 nits, and can go up to 4,000 nits or more, depending on the format and the device.
This means that HDR content can display much brighter highlights, such as the sun, fire, or explosions, and create a more realistic and immersive viewing experience.
However, not all devices can reach the same peak brightness level, and some HDR content may be too bright or too dim for some devices.
For example, if you watch HDR content on a device that has a peak brightness of 300 nits, you won’t be able to see the full range of brightness that the content offers, and some details may be clipped or washed out.
On the other hand, if you watch HDR content on a device that has a peak brightness of 1,000 nits, you may find the image too bright or uncomfortable for your eyes, especially in a dark room.
Therefore, it’s important to choose a device that has a suitable peak brightness level for your viewing environment and preferences, and to adjust the brightness settings accordingly.
You can also look for devices that have local dimming or backlight control features, which can improve the contrast and reduce the glare by dimming or turning off the backlight in some areas of the screen.
Color Gamut
Color gamut is the range of colors that a TV or monitor can display. It is measured by the percentage of the color space that the TV or monitor can cover.
The color space is a mathematical model that defines all the possible colors that can be perceived by the human eye.
The most common color spaces are Rec. 709 for SDR and Rec. 2020 for HDR.
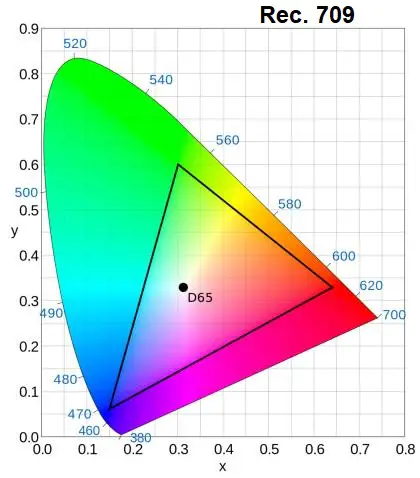
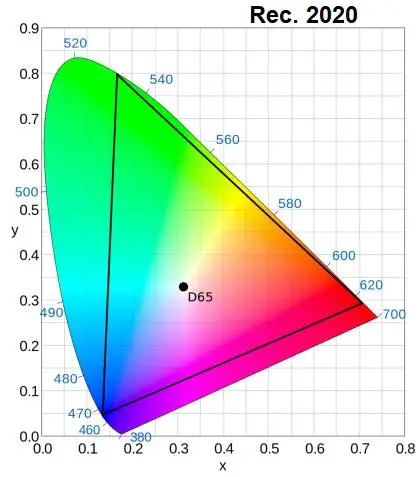
inside CIE 1931 x-y chromaticity diagram
HDR content can display more colors and shades, making the images more vibrant and natural.
For example, HDR content can show the subtle differences between different shades of green in a forest, while SDR content can only show a uniform green.
However, not all devices can display the full Rec. 2020 wide color gamut, and some HDR content may be too saturated or too dull for some devices.
For example, if you watch HDR content on a device that has a color gamut of 80% of Rec. 2020, you won’t be able to see the full range of colors that the content offers, and some colors may be missing or inaccurate.
On the other hand, if you watch HDR content on a device that has a color gamut of 100% of Rec. 2020, you may find the image too colorful or unnatural, especially if the content is not well-graded or calibrated.
Therefore, it’s important to choose a device that has a suitable color gamut for your viewing preferences and content, and to adjust the color settings accordingly.
You can also look for devices that have color management or calibration features, which can improve the color accuracy and consistency by matching the device’s color output to the content’s color input.
Color Depth
Color depth is the number of bits used to represent the color of each pixel.
It determines how many shades of each color the device can display.
The higher the color depth, the more color shades and hues the device can display.
SDR content uses 8-bit color depth, which means each pixel can have one of 256 shades of each color (red, green, and blue).
This results in a total of 16.7 million colors.
HDR content, on the other hand, uses 10-bit or 12-bit color depth, which means each pixel can have one of 1,024 or 4,096 shades of each color.
This results in a total of 1.07 billion or 68.7 billion colors, respectively.
It means that HDR content can display more subtle and nuanced colors, and avoid color banding or posterization artifacts, which are visible steps or blocks of colors in gradients or smooth transitions.
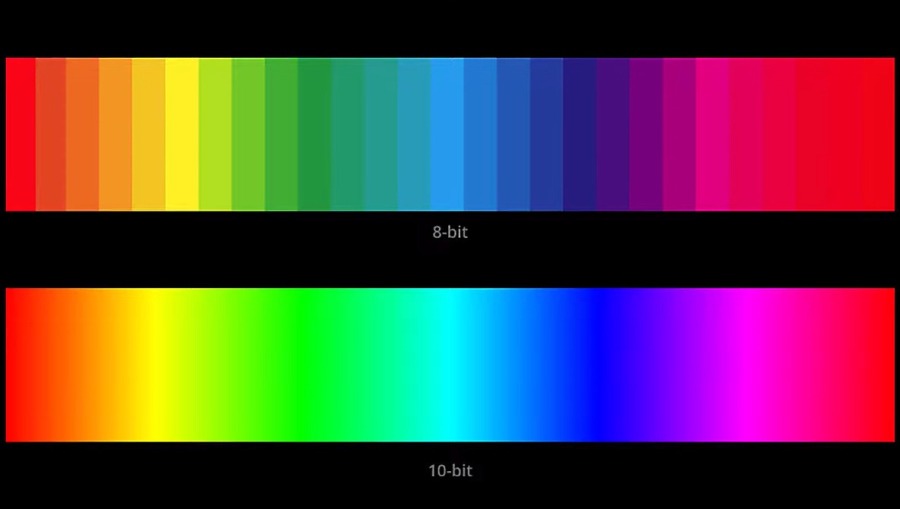

However, not all devices can display the same color depth, and some HDR content may be too detailed or too coarse for some devices.
For example, if you watch HDR content on a device that has an 8-bit panel, you won’t be able to see the full range of color shades that the content offers, and some colors may be dithered or approximated.
On the other hand, if you watch HDR content on a device that has a 10-bit or 12-bit panel, you may not notice much difference from an 8-bit panel, especially if the content is not well-graded or calibrated, or if the device has other limitations, such as low contrast or poor viewing angles.
Therefore, it’s important to choose a device that has a suitable color depth for your viewing preferences and content, and to adjust the color settings accordingly.
Gradient Handling
Gradient handling is the ability of a device to display smooth and continuous gradients or transitions between colors. It depends on the device’s color depth, color gamut, and processing capabilities.
SDR content has a limited color depth and color gamut, which means it can display fewer color shades and hues, and more prone to color banding or posterization artifacts.
HDR content has a higher color depth and color gamut, which means it can display more color shades and hues, and avoid color banding or posterization artifacts.
However, HDR content also has a higher dynamic range, which means it can display more contrast and brightness levels, and more prone to clipping or crushing artifacts, which are loss of details in very bright or very dark areas.
Therefore, it’s important to choose a device that has a good gradient handling for your viewing preferences and content, and to adjust the contrast and brightness settings accordingly.
You can also look for displays that have gamma or tone mapping features, which can improve the gradient handling by adjusting the luminance or brightness curve of the image.
The Pros and Cons of HDR and SDR

Movies
Movies are one of the most popular types of content that benefit from HDR, as they often have scenes with high contrast and wide color range, such as landscapes, sunsets, or explosions.
HDR can enhance the movie’s visual quality by displaying more realistic and immersive images, with brighter highlights, deeper shadows, and more details in both dark and bright areas.
HDR can also support more color shades and hues, which can create more vibrant and natural images, and avoid color banding or posterization artifacts.
However, HDR also has some drawbacks for movies, such as the compatibility and availability issues.
Not all movies are available in HDR, and not all devices are compatible with HDR, and some devices may have different HDR formats or capabilities.
For example, some devices may support HDR10, but not HDR10+ or Dolby Vision, which are more advanced HDR formats.
Some devices may also have lower peak brightness, color gamut, or color depth than the HDR content, which can affect the HDR performance.
Therefore, it’s important to check the device’s specifications and settings before watching HDR movies, and to choose the best HDR format and mode for your device and content.
Games
Games are another type of content that can benefit from HDR, as they often have scenes with high contrast and wide color range, such as environments, lighting, or effects.
HDR can enhance the game’s visual quality by displaying more realistic and immersive images, with brighter highlights, deeper shadows, and more details in both dark and bright areas.
HDR can also support more color shades and hues, which can create more vibrant and natural images, and avoid color banding or posterization artifacts.
However, HDR also has some drawbacks for games, such as the latency and performance issues.
HDR can increase the input lag or the delay between the controller and the screen, as the device needs more time to process the HDR signal and metadata.
HDR can also reduce the frame rate or the number of frames per second, as the device needs more power to render the HDR graphics and effects.
Therefore, it’s important to check the device’s capabilities and settings before playing HDR games, and to choose the best HDR mode and resolution for your device and game.
Photos
Photos are a type of content that can be both enhanced and degraded by HDR, depending on the source and the device.
HDR can enhance the photo’s visual quality by displaying more realistic and immersive images, with brighter highlights, deeper shadows, and more details in both dark and bright areas.
HDR can also support more color shades and hues, which can create more vibrant and natural images, and avoid color banding or posterization artifacts.
However, HDR can also degrade the photo’s visual quality by displaying too bright or too dim images, with clipped or crushed details in both dark and bright areas.
HDR can also display too saturated or too dull colors, with missing or inaccurate hues and shades.
This can happen if the photo is not taken or edited in HDR, or if the device is not compatible or calibrated for HDR.
Therefore, it’s important to check the photo’s format and metadata before viewing it in HDR, and to adjust the device’s settings accordingly.
How to Watch HDR Content on Your TV or Monitor
If you want to watch HDR content on your TV or monitor, you need to meet some requirements and follow some steps, such as:
Check the device’s specifications and features: It’s important to ensure your device supports HDR. You should also understand what HDR formats and modes it supports. Some devices may support HDR10 but not HDR10+ or Dolby Vision, which are more advanced HDR formats.
Devices may also have different HDR modes, such as HDR Standard, HDR Vivid, or HDR Cinema.
Check the content’s format and metadata: The content should be in HDR, and you should know what HDR format and metadata it has.
Some content may be in HDR10 but not HDR10+ or Dolby Vision, which have dynamic metadata. Content may also have different HDR levels, such as HDR400, HDR600, or HDR1000, indicating different peak brightness and color gamut values.
Check the connection and settings: The connection and settings should be compatible and optimized for HDR. Some devices may require a specific HDMI port, cable, or version to support HDR.
Enjoy the HDR content: Once everything is set up, you can enjoy the HDR content on your device. You can adjust the device’s settings, such as brightness, contrast, color, or gamma, to suit your viewing preferences and environment.
Some sources and services that offer HDR content:
Streaming services: Platforms like Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, Disney+, and YouTube offer HDR content, including movies, shows, or videos.
To access the HDR content, you need a compatible device, a fast internet connection, and a premium subscription.
It’s also important to check the content’s format and metadata, as some content may be in different HDR formats or levels.
Blu-ray discs: Some Blu-ray discs, such as 4K UHD Blu-ray discs, offer HDR content like movies or shows.
To access the HDR content, you need a compatible device like a 4K UHD Blu-ray player, and a compatible disc such as a 4K UHD Blu-ray disc. Again, checking the disc’s format and metadata is crucial, as some discs may be in different HDR formats or levels.
Games: Some games, including those on PS5, Xbox Series X, or PC, offer HDR content, such as graphics or effects.
You need a compatible device, such as a PS5, Xbox Series X, or PC, and a compatible game to access the HDR content.
As with the other sources, you also need to check the game’s format and metadata, as some games may be in different HDR formats or levels.
Q&A
Is 4K HDR or SDR?
4K refers to the resolution of the display, which is the number of pixels a screen can fit. It’s sometimes referred to as UHD or Ultra HD. HDR (High Dynamic Range), on the other hand, introduces a wider range of colors and brightness levels compared to SDR (Standard Dynamic Range) signals. So, 4K can be either HDR or SDR, depending on the range of colors and brightness levels the display can produce.
Is Netflix HDR or SDR?
Netflix supports both HDR and SDR content. However, to view HDR content, you need a compatible device that supports Netflix’s HDR features and a premium Netflix subscription.
Is SDR better than HDR?
SDR (Standard Dynamic Range) and HDR (High Dynamic Range) have different strengths. SDR has been the standard for many years and is widely compatible with various devices. On the other hand, HDR provides a higher level of contrast between light and dark images on the screen, offering a more realistic and vibrant picture. However, to fully enjoy HDR, you need an HDR-compatible display.
Is HDR better than 4K?
HDR and 4K refer to different aspects of the display. 4K refers to the resolution, while HDR refers to the display’s color and contrast range. HDR can provide a better viewing experience by offering more vibrant and lifelike colors and higher contrast, but 4K resolution can provide a sharper image. Ideally, for the best viewing experience, a display would be both 4K and HDR.
Should I turn HDR on or off?
If your display supports HDR (High Dynamic Range), it can provide a better viewing experience with more vibrant, lifelike colors and higher contrast. However, not all content is made for HDR, and viewing non-HDR content on an HDR setting could result in poorer image quality. Therefore, whether to turn HDR on or off depends on your display and the content you are viewing.
Does HDR look better?
HDR (High Dynamic Range) can provide a more vibrant, lifelike picture than Standard Dynamic Range (SDR). It increases the contrast between the lightest and darkest parts of the picture and expands the range of colors a screen can display. However, to enjoy the benefits of HDR, you need an HDR-compatible display and HDR content.
Read Next