High-definition (HD) and high-dynamic-range (HDR) are two terms frequently used when discussing display technology. While both contribute to improved visual quality, they achieve this through different mechanisms.
Understanding the differences between HD and HDR is crucial for making informed decisions when purchasing new displays or choosing content.
This article will break down the technical aspects of each technology, highlighting their unique benefits and helping you navigate the world of high-quality visuals.
What is HD?
HD, or High Definition, refers to a display resolution standard significantly higher than standard-definition (SD) video. It marked a significant leap in visual fidelity for television and other displays. The two most common HD resolutions (HD vs FHD) are:
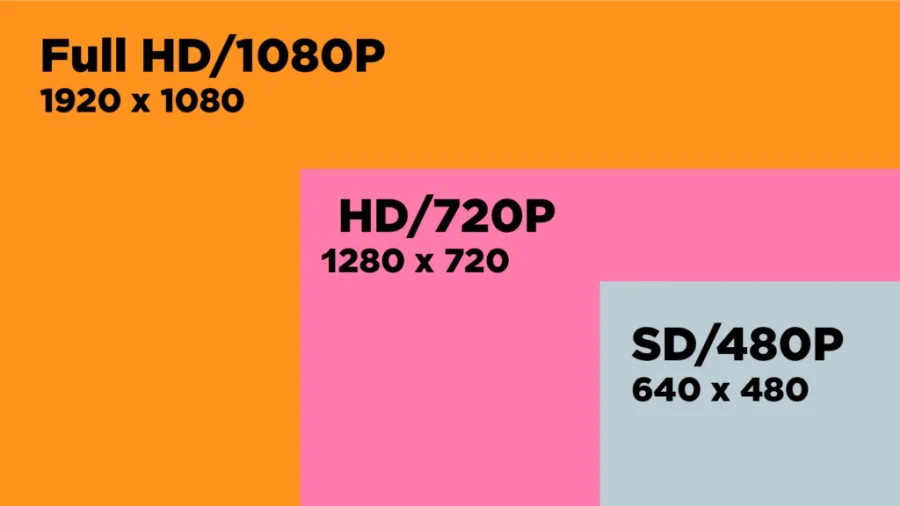
- 720p: This resolution boasts 1280 pixels horizontally and 720 pixels vertically, hence the name 720p. It’s often referred to as “HD Ready.”
- 1080p: Also known as Full HD, this resolution offers 1920 pixels horizontally and 1080 pixels vertically. It’s the most widely adopted HD resolution.
Historical Context and Development:
HD technology emerged in the late 20th century, with the development of high-definition television (HDTV) standards. The first broadcasting of HDTV began in Japan in 1991. The widespread adoption of HD began in the mid-2000s.
Technical Specifications:
| Resolution | Pixel Count | Aspect Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| 720p | 921,600 | 16:9 |
| 1080p | 2,073,600 | 16:9 |
Common Uses and Applications:
HD resolution is widely used in various applications, including:
- Television Broadcasting: Most TV channels broadcast in either 720p or 1080p.
- Blu-ray Discs: Blu-ray discs support 1080p resolution, offering high-quality movie experiences.
- Streaming Services: Many streaming platforms offer content in HD, including Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, and Hulu.
- Gaming Consoles: Modern gaming consoles support HD gaming, delivering immersive visuals.
What is HDR?
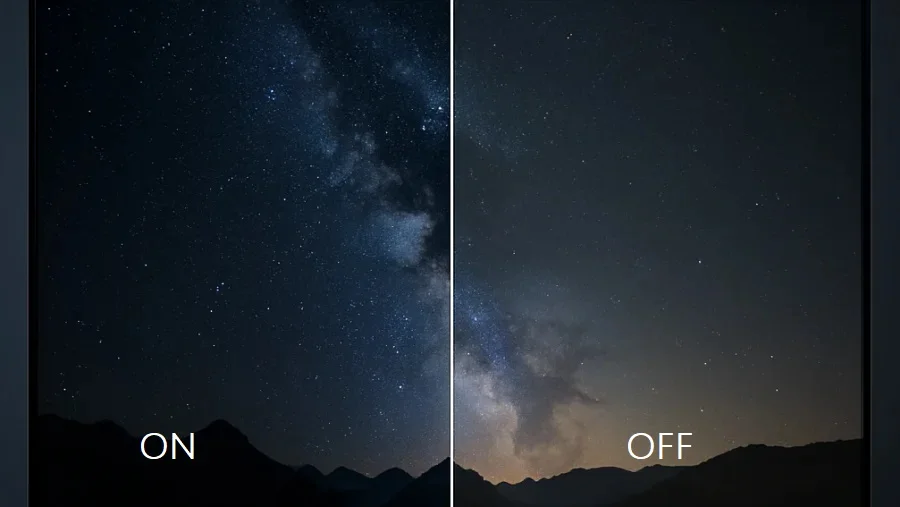
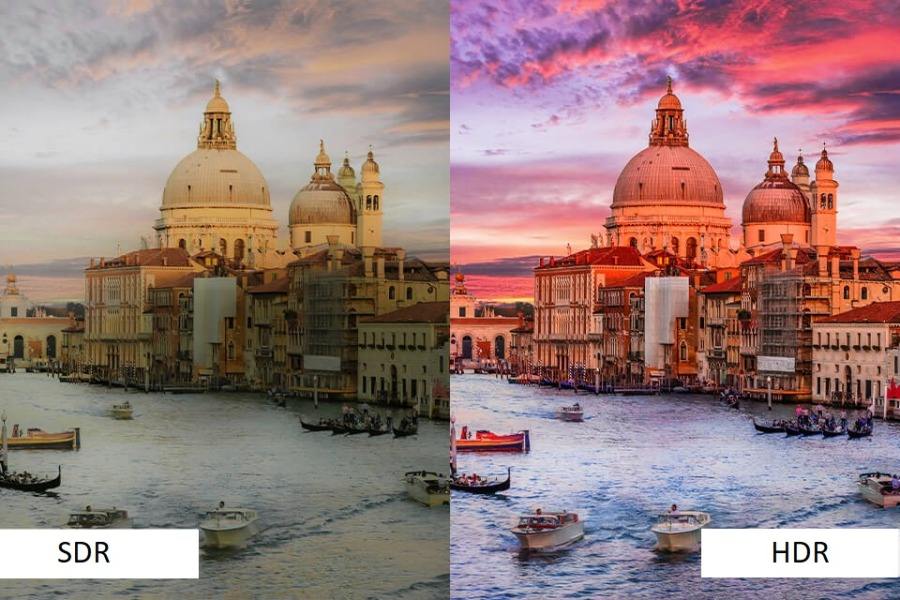
HDR, or High Dynamic Range, is a technology that enhances the dynamic range of an image, meaning the difference between the darkest blacks and the brightest whites. This results in a more realistic and visually appealing image with greater detail in both highlights and shadows.

Historical Context and Development:
While the concept of HDR photography has existed for much longer, HDR in displays emerged more recently. The first HDR-capable TVs were introduced around 2015.
Technical Specifications:
HDR doesn’t have a fixed resolution like HD. Instead, it focuses on expanding the color gamut, brightness, and contrast.
- Color Gamut: HDR displays can reproduce a wider range of colors compared to standard dynamic range (SDR)displays.
- Brightness: HDR content is mastered with higher peak brightness levels, allowing for more realistic and impactful highlights.
- Contrast: The increased dynamic range allows for greater contrast between light and dark areas, revealing more detail and depth.
Types of HDR:
Several HDR formats exist, each with its own specifications and requirements:
- HDR10: An open standard that is widely adopted and supported by most HDR-capable devices.
- HDR10+: An enhanced version of HDR10 that adds dynamic metadata, allowing for scene-by-scene adjustments to brightness and contrast.
- Dolby Vision: A proprietary format developed by Dolby Laboratories, offering even higher peak brightness and more advanced metadata for scene-by-scene optimization.
- HLG (Hybrid Log-Gamma): Primarily designed for broadcast television, HLG offers backward compatibility with SDR displays.
Display Standards (Brightness and Performance):
In addition to the formats above, several display standards indicate specific HDR performance levels:
- HDR400/HDR600/HDR1000: These standards, often used by the VESA organization, specify peak brightness levels for monitors and laptops. For example, HDR600 requires a display to have a peak brightness of at least 600 nits.
- HDR True Black 400/500/600: These standards, also by VESA, focus on black level performance for OLED HDR displays, indicating the ability to achieve deeper blacks for improved contrast.
Understanding these different formats and standards can help you choose the right HDR display and content for your needs.
Key Differences Between HD and HDR
The core difference between HD and HDR lies in what aspect of the image they enhance. HD focuses on resolution, which determines the clarity and detail of the image by increasing the number of pixels.
HDR, on the other hand, focuses on dynamic range, which improves the range of colors, brightness, and contrast. Think of it this way: HD provides the canvas with more detail, while HDR paints a more vibrant and nuanced picture on that canvas.
Resolution vs. Dynamic Range: A Deeper Dive
- HD and Pixel Count: HD is all about packing more pixels into the same screen space. Imagine a mosaic: the more tiles you have, the more intricate and detailed the image becomes. Similarly, HD increases the pixel count, resulting in sharper and more detailed images. The higher the resolution (e.g., 1080p vs. 720p), the more pixels are displayed, leading to finer details and reduced pixelation. This is particularly noticeable when viewing content on larger screens, where the increased pixel density prevents individual pixels from being visible.
- HDR and Enhanced Visuals: HDR doesn’t change the resolution or pixel count; it works with the existing pixels to enhance their visual impact. Think of it like upgrading your paints and brushes. Instead of adding more detail, HDR enhances the existing pixels by expanding the range of colors they can display and increasing the contrast between light and dark areas. This results in a more realistic and visually immersive experience with richer colors, brighter highlights, and deeper shadows. Details that might be lost in the shadows or blown out in highlights with standard dynamic range (SDR) content become visible with HDR, adding depth and realism to the scene.
Analogy: Photography vs. Painting
Consider the difference between a high-resolution photograph and a meticulously painted artwork. The high-resolution photograph captures a vast amount of detail, much like HD.
However, a skilled painter can use a limited palette of colors and a nuanced understanding of light and shadow to create a visually stunning and emotionally impactful artwork, much like HDR enhances the visual experience.
In essence, HD provides a sharper and clearer image, like a high-resolution photograph, while HDR makes the image more vibrant, lifelike, and detailed in terms of lighting and color variations, like a masterfully painted artwork. Both technologies contribute to a better viewing experience, but they achieve it through different means.
Benefits of HD
HD resolution has become the standard for visual media, offering several significant benefits:
Improved Image Clarity and Detail:
The most immediate benefit of HD is the significant improvement in image clarity and detail compared to standard definition. This is due to the higher pixel count, which allows for finer details to be displayed and reduces pixelation, especially on larger screens. This enhanced clarity makes images appear sharper, crisper, and more realistic.
Accessibility and Widespread Use:
HD technology is widely accessible and has become the standard for most displays, including televisions, monitors, smartphones, and streaming services. This widespread adoption makes it easy to find and enjoy HD content across various platforms and devices.
Cost Considerations:
Due to its maturity and widespread adoption, HD technology is relatively inexpensive to implement. HD displays are generally more affordable than their higher-resolution counterparts, such as 4K or 8K, making them accessible to a broader range of consumers.
Benefits of HDR
HDR technology offers a significant leap in visual quality, providing a more immersive and realistic viewing experience that goes beyond the simple sharpness offered by HD. It’s like the difference between looking at a photograph and seeing the scene in real life.
Enhanced Visual Experience with Better Contrast and Color: A More Immersive Reality
HDR’s primary benefit is its ability to significantly enhance the visual experience by expanding the dynamic range of an image. This translates to a more nuanced and detailed representation of light and color, bringing the on-screen image closer to what the human eye can perceive in the real world.
- Richer Colors: HDR displays can reproduce a wider range of colors, resulting in more vibrant and realistic visuals. Imagine a sunset bursting with vibrant oranges, reds, and purples, or a lush forest teeming with a multitude of greens. HDR captures these colors with greater accuracy and intensity, making the scene feel more alive and immersive.
- Brighter Highlights: HDR content can display brighter highlights without clipping, allowing for more realistic and impactful scenes. Think of the sun glinting off a car’s windshield or the shimmering reflection of light on water. HDR preserves these highlights with greater detail and brightness, adding a sense of realism and depth to the image.
- Deeper Shadows: HDR enhances shadow detail, revealing more information in darker areas of the image. This is particularly noticeable in scenes with complex lighting, such as a dimly lit room or a nighttime cityscape. HDR allows you to see details in the shadows that would otherwise be lost, creating a more realistic and engaging viewing experience.
Compatibility with Modern Content (Movies, Games): Experiencing Content as Intended
HDR is increasingly being used in modern content creation, including movies, TV shows, and video games. Many streaming services and Blu-ray discs now offer HDR content, allowing viewers to experience the full visual impact intended by the creators.
From the subtle nuances of a character’s expression in a dramatic scene to the explosive visual effects of a blockbuster action sequence, HDR brings the content to life with greater realism and fidelity.
Future-Proofing with Emerging Technologies: Investing in the Future of Visuals
HDR is a forward-looking technology that is compatible with emerging display technologies, such as OLED and Quantum Dot. These advanced display technologies leverage the benefits of HDR to deliver even more stunning visuals with perfect blacks, incredible contrast, and unparalleled color accuracy.
As these technologies continue to evolve, HDR will play a crucial role in delivering the best possible visual experience, ensuring that your investment in an HDR-capable display will continue to pay off for years to come.
Practical Considerations
While both HD and HDR offer significant visual improvements, several practical considerations should be taken into account when choosing a display or content:
Device Compatibility (TVs, Monitors, Smartphones):
- HD: HD is widely supported across various devices, including older models. Most TVs, monitors, and smartphones are HD-capable.
- HDR: HDR requires compatible displays and playback devices. Ensure that your TV, monitor, or smartphone specifically supports HDR technology. Look for labels like “HDR10,” “HDR10+,” “Dolby Vision,” or “HLG.”
Content Availability (Streaming Services, Blu-ray):
- HD: HD content is readily available from most streaming services and on Blu-ray discs.
- HDR: HDR content is becoming increasingly common, but it’s not as widely available as HD content. Streaming services like Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, and Disney+ offer a growing library of HDR content. Look for the HDR label on streaming titles or Blu-ray discs.
Cost and Investment:
- HD: HD displays are generally more affordable than HDR displays.
- HDR: HDR displays typically come at a premium due to the more advanced technology required. However, the price difference is decreasing as HDR becomes more mainstream. Consider the cost of the display and the availability of HDR content when making your decision.
Q&A
Is HDR the same as 1080p?
No, HDR and 1080p are different things. 1080p (Full HD) refers to the image resolution, specifically the number of pixels (1920×1080) that make up the picture’s sharpness. HDR (High Dynamic Range), on the other hand, relates to the range of colors and contrast levels – making whites brighter, blacks darker, and colors more vibrant. They are separate features that enhance different aspects of the image.
Does HDR give better quality?
Yes, HDR generally results in a visually superior image compared to standard dynamic range (SDR) content. It significantly expands the contrast range (brighter whites, deeper blacks) and allows for a wider, more nuanced spectrum of colors. This leads to a picture that looks more realistic, vibrant, and detailed in both bright and dark areas, enhancing the overall viewing experience.
Is HDR10 Full HD?
No, HDR10 is not inherently Full HD (1080p). HDR10 is a specific format or standard for High Dynamic Range video, focusing on color and contrast information. Full HD (1080p) refers to the screen resolution (1920×1080 pixels). While you can have content and displays that are both Full HD and support HDR10, HDR10 is also commonly found (and often more impactful) on higher resolutions like 4K UHD. They are distinct specifications.
Read Next











