4K resolution delivers exceptional image sharpness and detail, and is rapidly setting the standard in the field of visual content.
We will explore what 4K resolution is, how it evolved, how it compares with other resolutions, its challenges and opportunities, and how HDR enhances 4K resolution.
By the end of this article, you will have a better understanding of why 4K is the future of visual entertainment, and how you can enjoy it on your devices.
What is 4K Resolution?
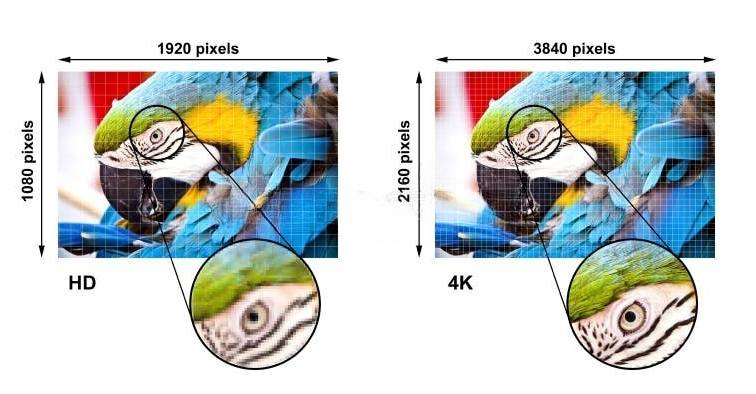
4K resolution, also known as 4K or 4K Ultra HD, is a display resolution that has approximately 4,000 pixels horizontally and approximately 2,000 pixels vertically, resulting in a total of about 8 million pixels.
This is four times the number of pixels of Full HD (1920 x 1080), which is the most common display resolution today. More pixels mean more detail, clarity, sharpness, and depth, which translate to a more realistic and immersive viewing experience.
However, 4K resolution is not a single, uniform standard. There are different variations of 4K resolution, depending on the context and industry. For example, in digital cinema, 4K resolution is defined by the Digital Cinema Initiatives (DCI) as 4096 x 2160, which has an aspect ratio of 1.9:1.
This is slightly wider than the 16:9 aspect ratio of most TVs and monitors, which use 3840 x 2160 as the 4K resolution which is also known as 4K UHD (Ultra High Definition), and is the most widely used 4K resolution for consumer media and devices.
4K content and devices available today
4K movies and TV shows: Many streaming services, such as Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, Disney+, and YouTube, offer 4K content, ranging from original productions to remastered classics.
You can also watch 4K content on Blu-ray discs, which have a higher storage capacity and bitrate than DVDs.
4K TVs and monitors: 4K TVs can do more than just stream the latest shows. It’s also ideal for connecting a home theater system, gaming console, computer, or other devices.
There are many models and brands of 4K TVs and monitors to choose from, with different specifications, such as size, refresh rate, contrast ratio, color gamut, and brightness.
Some 4K TVs and monitors also support HDR (high dynamic range), which we will discuss later.
4K cameras and camcorders: You can capture your own 4K videos and photos with 4K cameras and camcorders, which have higher resolution and quality than HD cameras and camcorders. Some smartphones also have 4K cameras, which allow you to record 4K videos and take 4K selfies.

4K gaming consoles and PCs: You can play 4K games on 4K gaming consoles, such as the PlayStation 5 and the Xbox Series X, or on 4K gaming PCs, which have powerful graphics cards and processors. 4K games have more realistic graphics, animations, and effects than HD games.
The Evolution of 4K Resolution
4K resolution is not a new technology. It has been around for more than two decades, but it was not until recently that it became accessible and affordable for consumers.
The history of 4K can be traced back to the following milestones:

- 2003: The first 4K digital camera was the DALSA Origin built by DALSA Corporation, which was presented at NAB Show 2003.
- 2004: Sony starting to offer first 4K digital cinema projectors.
- 2010: YouTube began supporting 4K for video uploads in response to the emergence of 4K cameras from leading manufacturers.
- 2012: First 4K TVs introduced to the market.
- 2015: First 4K smartphone was released, Sony Xperia Z5 Premium, which had a 5.5-inch 4K screen and a 4K rear camera.
- 2016: The first Ultra HD Blu-ray players and discs were launched. This was a new optical disc format that supported video with 4K resolution and HDR.
- 2016: First 4K gaming console Sony PlayStation 4 Pro, upgraded version of the PlayStation 4 with improved hardware to enable 4K rendering.
- 2018: FuboTV became the first live-TV streaming service to support 4K HDR video (2018 World Cup).
4K Standards
4K resolution is not a single, uniform standard. There are different formats, depending on the context and industry. Some of the most common 4K standards:
| Standard | Industry | Resolution | Aspect Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| DCI 4K | Cinema | 4096 x 2160 | 1.9:1 |
| SMPTE UHDTV1 | Broadcast | 3840 x 2160 | 16:9 |
| ITU-R UHDTV | Telecom | 3840 x 2160 | 16:9 |
| CEA Ultra HD | Consumer | 3840 x 2160 | 16:9 |
DCI 4K: This is the 4K standard used by the digital cinema industry, and is defined by the Digital Cinema Initiatives (DCI) as 4096 x 2160, with an aspect ratio of 1.9:1.This is slightly broader than the 16:9 aspect ratio commonly found in most televisions and monitors, which use 3840 x 2160 as the 4K resolution.
SMPTE UHDTV1: This is the 4K standard used by the broadcast and production industry, and is defined by the Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers (SMPTE) as 3840 x 2160, with an aspect ratio of 16:9. This is the same as the 4K UHD resolution used by most TVs and monitors, and is the most widely used 4K resolution.
ITU-R UHDTV: This is the 4K standard used by the telecommunications industry, and is defined by the International Telecommunication Union Radiocommunication Sector (ITU-R) as 3840 x 2160, with an aspect ratio of 16:9. This is the same as the SMPTE UHDTV1 and 4K UHD resolutions, and is also widely used for consumer media and devices.
CEA Ultra HD: This is the 4K standard used by the consumer electronics industry, and is defined by the Consumer Electronics Association (CEA) as 3840 x 2160, with an aspect ratio of 16:9. This is the same as the SMPTE UHDTV1, ITU-R UHDTV, and 4K UHD resolutions, and it is also commonly utilized in consumer media and devices.
4K vs Other Resolutions
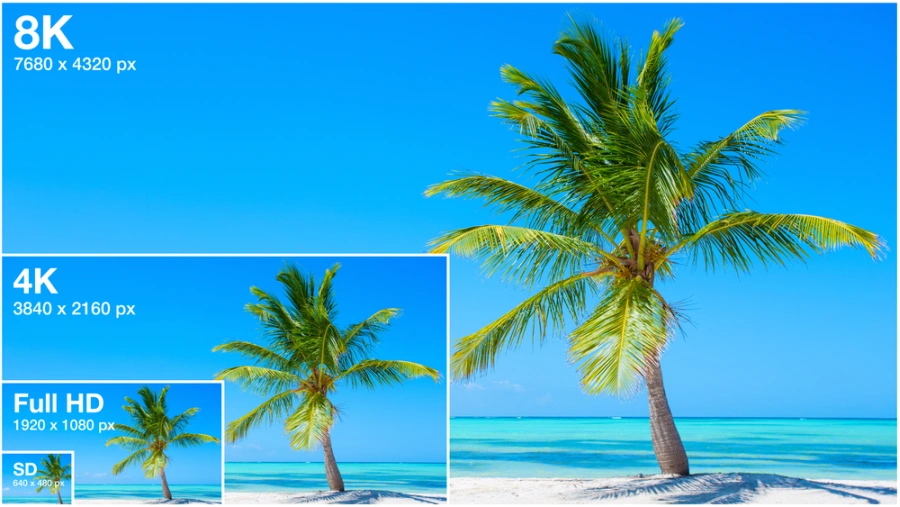

4K in comparison with some other common display resolutions:
| Designation | Resolution | Aspect Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| 4K UHD | 3840 x 2160 | 16:9 |
| 5K | 5120 x 2880 | 16:9 |
| QHD | 2560 x 1440 | 16:9 |
| WUXGA | 1920 x 1200 | 16:10 |
| Full HD | 1920 x 1080 | 16:9 |
4K and 5K resolutions can display more details and sharpness on the screen. However, they also require more processing power and bandwidth to render and stream the content.
QHD is lower than 4K and 5K, but still offer a significant improvement over Full HD and WUXGA resolutions. It is also more compatible with most devices and platforms.
WUXGA resolution has a slightly longer field of view than Full HD, which gives more space for multitasking and productivity.
Full HD resolution is the most common and widely used resolution today, but it may not be able to keep up with the increasing demand for higher quality and immersive content.
Challenges and Opportunities of 4K
4K resolution is not without its challenges and opportunities. As the demand for 4K content and devices grows, so do the issues and solutions related to bandwidth, storage, compatibility and cost.
Bandwidth: 4K resolution requires a lot of bandwidth to stream or download the content, especially if it is combined with HDR. According to Netflix, streaming 4K content requires at least 15 Mbps of internet speed, this can affect the data cap and cost of the internet service.
Storage: 4K content requires a lot of storage space to store the content, as it has four times more pixels than Full HD content. For example, a 4K Blu-ray disc can hold up to 100 GB of data, while a 4K video file depending on the length, quality, and format can reach over that limit.
Compatibility: 4K resolution requires a compatible device and display to enjoy the content, especially if it is combined with HDR. For example, a 4K TV or monitor requires an HDMI 2.0 or higher port, a HDCP 2.2 or higher protection, and a HDR10 or Dolby Vision support, to display the 4K content properly. Therefore 4K may not be supported by older or cheaper devices or displays.
Cost: 4K content and devices require a high cost, as they have higher quality and performance. For example, a 4K camera or smartphone can cost from hundreds to thousands of dollars, while a 4K TV or monitor can cost from thousands to tens of thousands of dollars.
Buying or using 4K content and devices may incur additional costs, such as internet service, streaming service and storage devices.
4K also offers many opportunities for innovation and improvement. As the technology and industry evolve, so do the solutions and benefits for the users. Some of the possible and benefits are:
Improving the internet speed and reducing the internet cost, which can enable faster and smoother streaming of 4K content.
New and efficient compression and encoding techniques, which can reduce the bandwidth and storage requirements of 4K content such as HEVC, VP9, AV1 and H.264.
Lowering the price and increasing the quality of 4K devices, which can make 4K content more affordable and accessible for the users.
HDR and 4K Resolution
HDR, or high dynamic range, is a technology that complements 4K resolution, and enhances the visual quality and immersion of the content.
HDR can capture and reproduce the details and nuances of the dark and bright areas, that are often lost or distorted in standard dynamic range (SDR) content and devices.
This technology can be applied to both video and photo content, and can be combined with 4K resolution to create the ultimate viewing experience.

HDR content and devices require a higher level of quality and performance than SDR content and devices. HDR content requires a higher bit depth, which is the number of bits used to represent the color of each pixel.
A higher bit depth means a larger color space or wider color gamut, which is the range of colors that can be displayed. For example, SDR content typically uses 8-bit color, which can display 16.7 million colors, while HDR content typically uses 10-bit or 12-bit color, which can display 1.07 billion or 68.7 billion colors, respectively.
HDR devices require a higher peak brightness, which is the maximum amount of light that can be emitted by the display. A higher peak brightness means a higher contrast ratio, which is the difference between the darkest and brightest parts of the image.
SDR devices typically have a peak brightness of about 100 nits, which is the unit of luminance or brightness. HDR devices, on the other hand, can have a theoretical peak brightness of up to 10,000 nits, which is 100 times more than SDR devices.
This means that HDR devices can display a wider range of brightness levels, from the darkest blacks to the brightest whites, without losing detail or quality.
However, HDR content and devices require a specific HDR format, which is the way the HDR data is encoded and decoded.
Each HDR formats has its own features and specifications:
| HDR Format | Description |
|---|---|
| HDR10 | The most common and basic HDR format. It uses static metadata, which is the information about the HDR settings of the content. |
| HDR10+ | An enhanced version of HDR10. It uses dynamic metadata, which is the information that can change according to each scene or frame of the content. |
| Dolby Vision | A proprietary HDR format. It uses dynamic metadata and a higher bit depth of 12 bits, which can display more colors than HDR10 or HDR10+. |
| HLG | A hybrid HDR format. It uses no metadata, but it can be compatible with both HDR and SDR devices. |
Therefore, playing or displaying HDR content requires matching the HDR format of the content and the device.
Reproducing HDR content also requires supporting the HDMI 2.0a or higher standard, which is the interface that connects the content and the device. This standard can support the higher bandwidth and data rate that HDR content requires.
Conclusion
4K resolution isn’t just a step up—it’s a leap into a sharper, more gripping world of entertainment that hooks you in and doesn’t let go.
As explored throughout this article, its superior image quality not only enhances user satisfaction but also paves the way for a more captivating and realistic engagement with content.
While some challenges remain, the opportunities presented by 4K—especially when paired with HDR technology’s enhanced contrast are transforming how we perceive and enjoy media.
These advancements herald a bold future for entertainment, promising viewers an lifelike experience that redefines what’s possible on screen.
Q&A About 4K
Is 4K 3840×2160 or 4096×2160?
4K can refer to two different resolutions. In the movie projection industry, 4K refers to a resolution of 4096×2160. However, in consumer electronics like TVs and monitors, 4K usually refers to a resolution of 3840×2160, which is also known as 4K UHD or Ultra High Definition.
What does 4K stand for?
4K stands for a resolution that has approximately 4000 pixels in width. The term comes from the movie industry, where it originally referred to a resolution of 4096×2160.
Is 4K the highest resolution?
No, 4K is not the highest resolution. There are higher resolutions such as 5K (5120 x 2880), 8K (7680 x 4320), and even 16K (15360 x 8640). However, the visual improvement from 4K to higher resolutions is less noticeable, especially on smaller screens or from a typical viewing distance.
Is 2160p the same as 4K?
Yes, 2160p is often used interchangeably with 4K. The ‘p’ stands for progressive scan, and 2160 refers to the number of vertical pixels. In the case of 4K UHD (3840×2160), there are 2160 vertical pixels.
Is Ultra HD and 4K the same?
Ultra HD (UHD) and 4K are often used interchangeably, but they technically refer to slightly different resolutions. UHD typically refers to a resolution of 3840×2160, while 4K in the movie industry refers to 4096×2160.
Can you tell the difference between 4K and 1080p?
The difference between 4K and 1080p can be noticeable, especially on larger screens or when sitting closer to the screen. 4K has four times the number of pixels as 1080p, resulting in a much sharper and more detailed image. However, the difference may not be as noticeable on smaller screens or from a distance.
Read Next