V-SYNC is a feature that can improve your gaming experience by eliminating screen tearing, but it also has some drawbacks. Here is a simple guide to help you understand what V-SYNC is and whether you should enable it or not.
What Is V-SYNC And How Does It Work?
V-SYNC stands for Vertical Synchronization, and it is a feature that synchronizes your graphics card’s frame rate with your monitor’s refresh rate.
This means that your graphics card will only send frames to your monitor when it is ready to display them, instead of sending as many frames as it can.
The purpose of V-SYNC is to prevent screen tearing, which is a visual artifact that occurs when your frame rate is higher than your monitor’s refresh rate.
Screen tearing happens when your monitor displays parts of two or more frames at the same time, creating a horizontal line that splits the image.

By enabling V-SYNC, you can ensure that your monitor displays only one full frame at a time, resulting in a smooth and consistent image. However, V-SYNC also has some disadvantages that you should be aware of.
Pros And Cons
The main benefit of V-SYNC is that it eliminates screen tearing, which can be very distracting and annoying for some gamers. Screen tearing can also affect your gameplay, as it can make it harder to aim, track, and react to fast-moving objects on the screen.
The main drawback of V-SYNC is that it introduces input lag, which is the delay between your input (mouse, keyboard, controller, etc.) and the corresponding action on the screen.
Input lag can affect your gaming performance, as it can make it feel like your controls are sluggish and unresponsive.
Input lag is caused by V-SYNC because your graphics card has to wait for your monitor to finish displaying the current frame before sending the next one. This means that your graphics card is always one frame behind your monitor, creating a gap between your input and the output.
Another drawback of V-SYNC is that it can cause stuttering, which is a sudden drop or fluctuation in your frame rate.
Stuttering can occur when your graphics card cannot keep up with your monitor’s refresh rate, and it has to repeat the same frame or skip a frame to catch up.
Stuttering can also affect your gaming experience, as it can make the game feel choppy and unstable. Stuttering can also affect your input lag, as it can make it unpredictable and inconsistent.
When Should You Enable Or Disable V-SYNC?
The answer to this question depends on several factors, such as your personal preference, your PC rig, your monitor, and the game you are playing. Here are some general guidelines to help you decide:
- You should enable V-SYNC if you notice prominent screen tearing in video games, and if you can maintain a higher or equal FPS to your monitor’s maximum refresh rate. This way, you can enjoy a tear-free and smooth gaming experience, without sacrificing too much input lag or performance.
- You should disable V-SYNC if you value input lag and performance over image quality, and if you are playing competitive FPS games where every millisecond counts. This way, you can have more responsive and fluid controls, and higher FPS, at the cost of some screen tearing.
- You should also disable V-SYNC if your frame rate is mostly below your monitor’s maximum refresh rate anyway, as V-SYNC will only increase your input lag and stuttering, without providing any benefit.
Are There Any Alternatives To V-SYNC?
Yes, there are some alternatives to V-SYNC that can offer a better balance between image quality, input lag, and performance. Some of these alternatives are:
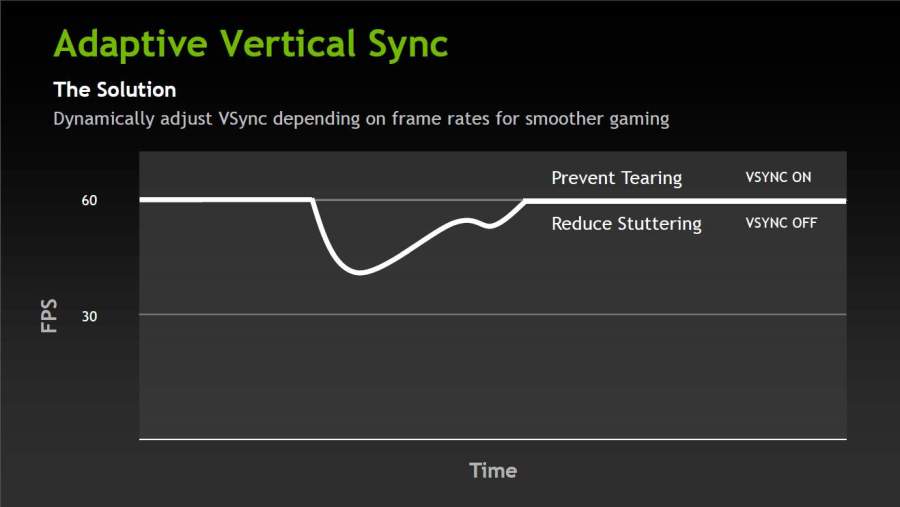
- Adaptive V-SYNC: This is a feature that is available on some NVIDIA graphics cards, and it can be enabled in the NVIDIA driver settings. Adaptive V-SYNC works by turning V-SYNC on when your frame rate is higher than your monitor’s refresh rate, and turning it off when it is lower. This way, you can avoid screen tearing when you have high FPS, and avoid stuttering when you have low FPS.
- Fast Sync: This is another feature that is available on some NVIDIA graphics cards, and it can be enabled in the NVIDIA driver settings. Fast Sync works by allowing your graphics card to render as many frames as it can, but only sending the most recent frame to your monitor. This way, you can avoid screen tearing and stuttering, while having minimal input lag. However, Fast Sync can also cause some micro-stuttering, which is a subtle variation in frame times that can make the game feel less smooth.
- Enhanced Sync: This is a feature from AMD that helps gamers minimize screen tearing while decreasing the latency and stutter of traditional V-sync. Enhanced Sync works best when your framerate exceeds your display’s refresh rate, providing a tear-free experience at an ultra-low latency.
- G-SYNC and AMD FreeSync: These are features that are available on some monitors, and they require compatible graphics cards to work. G-SYNC and FreeSync work by dynamically adjusting your monitor’s refresh rate to match your graphics card’s frame rate. This way, you can have a tear-free, stutter-free, and low-latency gaming experience, regardless of your FPS. However, G-SYNC and FreeSync monitors are usually more expensive than regular monitors, and they have some limitations, such as a certain refresh rate range and compatibility issues.
Conclusion
V-SYNC is a feature that can improve your gaming experience by eliminating screen tearing, but it also has some drawbacks, such as input lag and stuttering. Whether you should enable it or not depends on your personal preference, your PC rig, your monitor, and the game you are playing.
Some alternatives to V-SYNC, such as Adaptive V-SYNC, Fast Sync, Enhanced Sync, G-SYNC and AMD FreeSync, can offer a better balance between image quality, input lag, and performance, but they also have some pros and cons that you should consider.
Ultimately, the best way to find out what works best for you is to try different settings and see how they affect your gaming experience.
Common Questions about V-Sync
Is it better to have VSync on or off?
It depends on your preference and hardware. VSync can prevent screen tearing, which is when your display shows parts of multiple frames at once. However, VSync can also lower your FPS and increase input lag, which can affect your performance and responsiveness in games. If you have a powerful GPU and a high refresh rate monitor, you may not need VSync at all. If you have a weaker GPU or a low refresh rate monitor, you may want to use VSync to avoid screen tearing.
What does VSync do?
VSync, short for vertical synchronization, is a technology that synchronizes the refresh rate of your display with the frame rate of your GPU. This means that your display will only show a new frame when it is ready, and not in the middle of a refresh cycle. This can eliminate screen tearing, which is when your display shows parts of multiple frames at once, creating a distorted image.
Does VSync increase FPS?
No, VSync does not increase FPS. In fact, VSync can lower your FPS, as it limits your GPU’s frame rate output to your monitor’s refresh rate. For example, if you have a 60Hz monitor, VSync will cap your FPS to 60, even if your GPU can render more frames per second. This can cause stuttering and input lag, especially if your GPU’s frame rate fluctuates below and above your monitor’s refresh rate.
Does VSync increase input lag?
Yes, VSync can increase input lag, which is the delay between your input and the corresponding action on the screen. This is because VSync introduces a buffer between your GPU and your display, which can delay the delivery of frames. The higher the buffer, the higher the input lag. For example, if you use double-buffered VSync, which has two buffers, your input lag can be up to two frames. If you use triple-buffered VSync, which has three buffers, your input lag can be up to three frames. Input lag can affect your reaction time and accuracy in games, especially in fast-paced and competitive genres.
Do I need VSync for 144Hz?
Not necessarily. While VSync prevents screen tearing by locking your frame rate to the monitor’s refresh rate (144 FPS in this case), it often introduces input lag, which can be detrimental in fast-paced games. At 144Hz, the potential for tearing is already reduced compared to lower refresh rates. Many users prefer to leave VSync off or, ideally, use Adaptive Sync technologies like G-Sync or FreeSync if available, as these eliminate tearing without the added input lag.
Which is better G-Sync or VSync?
G-Sync (and its counterpart, FreeSync) is significantly better than traditional VSync. While both aim to eliminate screen tearing, VSync achieves this by forcing your graphics card to wait for the monitor, which often introduces noticeable input lag and can cause stuttering if your frame rate drops below the refresh rate. G-Sync, however, dynamically adjusts your monitor’s refresh rate to match the frame rate output by your compatible Nvidia GPU, eliminating tearing and stuttering without adding significant input lag, resulting in a much smoother and more responsive gaming experience.
Read Next