Display resolution plays a crucial role in our increasingly digital world.
From the smartphones in our pockets to the massive televisions in our living rooms, the clarity and detail of the content we consume are directly tied to the resolution of the display.
This article aims to demystify the terms HD, 2K, and 4K, providing a comprehensive understanding of their differences, uses and technical specifications.
What is HD?
HD, short for High Definition, marked a significant leap forward in display technology, offering a substantial improvement over the previously prevalent standard definition (SD) resolution.
HD encompasses a range of resolutions, but the most commonly encountered are 720p and 1080p (HD vs FHD).
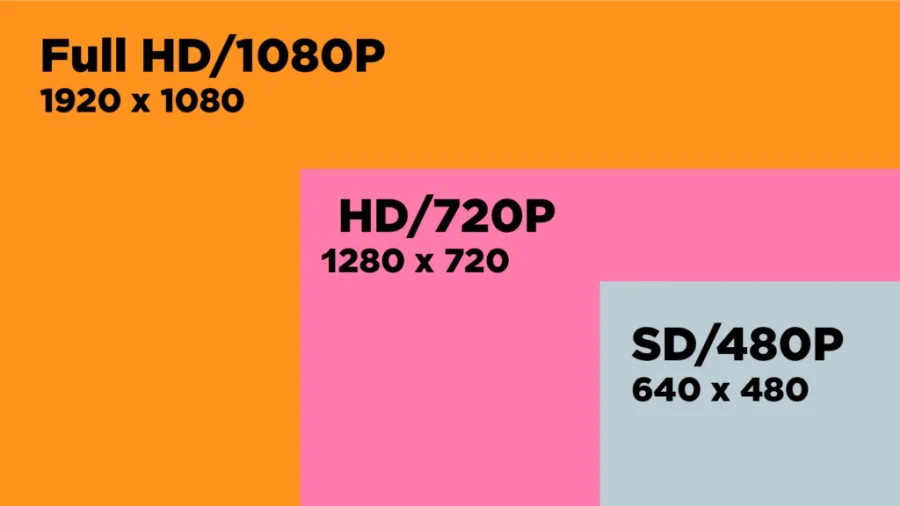
- 720p: This resolution, often referred to as HD Ready, has a resolution of 1280 x 720 pixels, totaling 921,600 pixels.
- 1080p: Also known as Full HD, this resolution boasts 1920 x 1080 pixels, resulting in a total of 2,073,600 pixels.
HD resolution became widely adopted in the early 2000s, with the advent of Blu-ray discs and the transition to digital television broadcasting. Today, HD remains prevalent in various applications, including:
- Older Televisions: Many televisions manufactured before the widespread adoption of 4K still utilize HD resolutions.
- Budget Smartphones and Tablets: Entry-level and budget-friendly mobile devices often feature HD displays to keep costs down.
- Streaming Services: Some streaming platforms offer content in HD resolution, especially for lower bandwidth connections.
Pros of HD Resolution:
- Lower Bandwidth Requirements: Compared to higher resolutions, HD content requires less bandwidth for streaming and downloading.
- Lower Power Consumption: Devices with HD displays generally consume less power than those with higher resolutions.
- Cost-Effective: HD displays are typically more affordable than 2K or 4K displays.
Cons of HD Resolution:
- Lower Pixel Density: Compared to 2K and 4K, HD displays have a lower pixel density, resulting in less detail and sharpness, particularly on larger screens.
- Less Immersive Experience: The lower detail can lead to a less immersive viewing experience, especially for content designed for higher resolutions.
What is 2K?
The term 2K resolution often refers to resolutions that have a horizontal pixel count of approximately 2000 pixels.
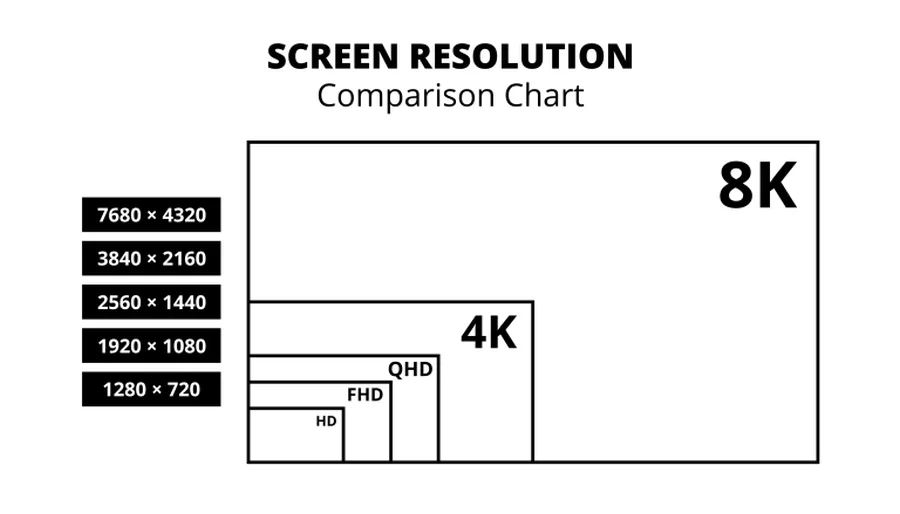
The most common 2K resolution is QHD (Quad HD), which stands for 2560 x 1440 pixels, totaling 3,686,400 pixels. This is also often referred to as 1440p.
2K resolution emerged as a stepping stone between HD and 4K, offering a noticeable improvement in image quality without the significant hardware demands of 4K. Devices that commonly utilize 2K resolution include:
- Gaming Monitors: 2K resolution has gained popularity among PC gamers, providing a balance between visual fidelity and performance.
- Mid-Range Smartphones: Many mid-range smartphones feature 2K displays, offering sharper visuals than HD counterparts.
- Some High-End Laptops: Certain laptops, particularly those geared towards creative professionals, may incorporate 2K displays.
Pros of 2K Resolution:
- Increased Detail and Sharpness: Compared to HD, 2K provides a noticeable improvement in detail and sharpness, resulting in clearer images and text.
- Improved Gaming Experience: The higher resolution enhances the gaming experience, providing more immersive visuals.
- Balanced Performance: 2K generally requires less processing power than 4K, making it a suitable option for a wider range of devices.
Cons of 2K Resolution:
- Higher Bandwidth Requirements: Streaming and downloading 2K content requires more bandwidth than HD.
- Increased Power Consumption: Devices with 2K displays generally consume more power than HD counterparts.
- Higher Cost: 2K displays are typically more expensive than HD displays.
What is 4K?
4K resolution, often referred to as Ultra High Definition (UHD), represents the current pinnacle of mainstream display technology.
The most common 4K resolution is 3840 x 2160 pixels, totaling 8,294,400 pixels. This is also frequently referred to as 2160p.
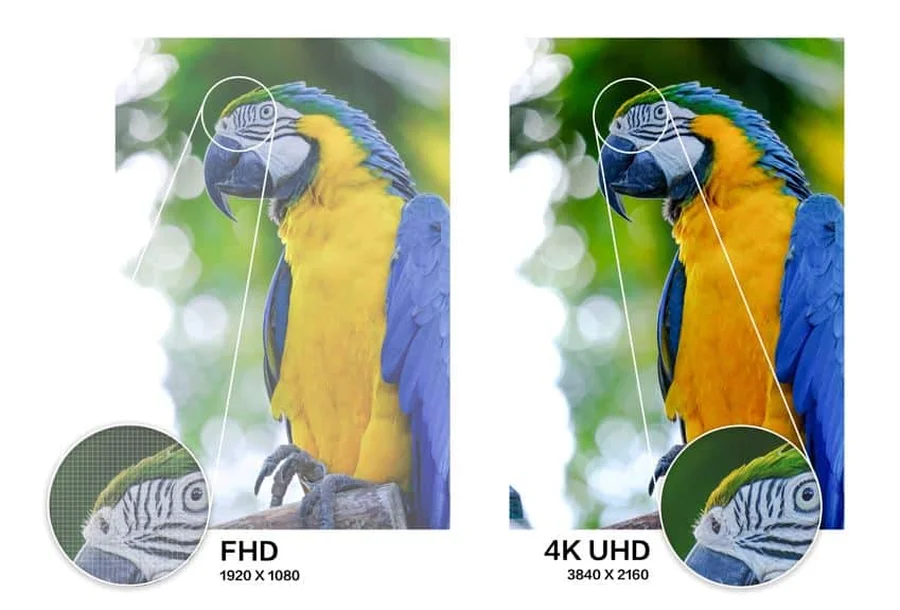

4K resolution started gaining traction in the early 2010s, with the introduction of 4K televisions and the emergence of streaming services supporting 4K content.
Today, 4K is becoming increasingly prevalent in various devices, including:
- High-End Televisions: Most modern high-end televisions feature 4K resolution, offering stunning picture quality.
- Professional Monitors: 4K monitors are widely used by professionals in fields such as video editing, graphic design, and photography.
- Flagship Smartphones: Many flagship smartphones now boast 4K displays, allowing for incredibly detailed mobile viewing experiences.
Pros of 4K Resolution:
- Exceptional Detail and Sharpness: 4K provides unparalleled detail and sharpness, making images and videos appear incredibly lifelike.
- Highly Immersive Experience: The high pixel density creates a truly immersive viewing experience, especially on larger screens.
- Future-Proofing: Investing in 4K ensures compatibility with the latest content and provides a degree of future-proofing.
Cons of 4K Resolution:
- High Bandwidth Requirements: Streaming and downloading 4K content requires significant bandwidth.
- Significant Power Consumption: Devices with 4K displays consume considerably more power than those with lower resolutions.
- High Cost: 4K displays are generally the most expensive option.
Comparison of HD, 2K, and 4K
| Feature | HD (1080p) | 2K (1440p) | 4K (2160p) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resolution | 1920 x 1080 | 2560 x 1440 | 3840 x 2160 |
| Total Pixels | 2,073,600 | 3,686,400 | 8,294,400 |
| Pixel Density | Lower | Medium | Higher |
| Image Clarity | Good | Very Good | Excellent |
| Bandwidth Needs | Low | Medium | High |
| Power Consumption | Low | Medium | High |
| Cost | Lower | Medium | Higher |
Choosing the Right Resolution
Selecting the appropriate display resolution depends on several factors, including:
- Usage Scenario: Casual viewing, gaming, professional work, etc.
- Budget: The cost of devices increases with higher resolutions.
- Device Compatibility: Ensure your devices (e.g., gaming consoles, streaming devices) support the desired resolution.
Recommendations:
- Casual Viewers: HD might suffice for casual viewing on smaller screens.
- Gamers: 2K or 4K offers a more immersive gaming experience, depending on your hardware capabilities.
- Professionals: 4K is often preferred for tasks requiring high detail and accuracy.
Future Trends in Display Technology
8K Resolution and Beyond
8K resolution, boasting a staggering 7680 x 4320 pixels (33,177,600 total pixels), represents the next frontier in display resolution.
While 8K displays are currently available, their adoption is limited due to factors such as high cost, lack of readily available 8K content, and demanding hardware requirements.
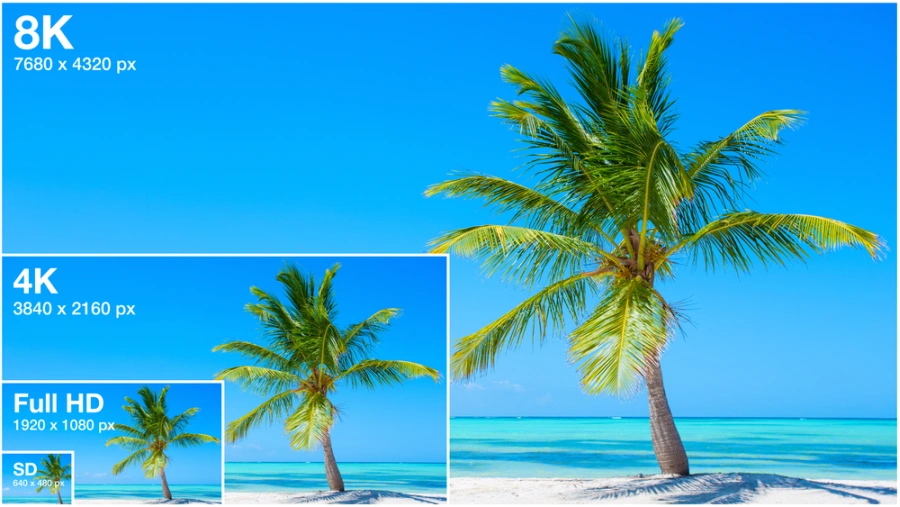

However, as technology advances and prices decrease, 8K is expected to gradually gain traction in the coming years, offering an unprecedented level of detail and realism.
Beyond 8K, research and development are already underway for even higher resolutions, such as 16K, hinting at a future where displays can render images with an almost indistinguishable level of detail compared to the real world.
High Dynamic Range (HDR)
HDR technology focuses on expanding the range of colors and contrast that a display can reproduce. By displaying a wider range of brightness levels and a wider color gamut, HDR content appears more vibrant, realistic, and immersive.
HDR is becoming increasingly prevalent in televisions, monitors, and smartphones, complementing higher resolutions by enhancing the overall visual experience.
As HDR technology matures, we can expect even more refined implementations that further enhance the realism and visual impact of displayed content.
High Refresh Rates
Refresh rate, measured in Hertz (Hz), refers to the number of times a display refreshes its image per second. Higher refresh rates result in smoother motion, particularly noticeable in fast-paced content such as gaming and action movies.
While 60Hz has long been the standard refresh rate, displays with refresh rates of 120Hz, 144Hz, and even higher are becoming increasingly common, especially in gaming monitors.
These higher refresh rates contribute to a more fluid and responsive visual experience, reducing motion blur (GTG vs MPRT) and enhancing overall clarity.
Advancements in Panel Technology
Beyond resolution, advancements in panel technologies themselves are also shaping the future of displays.
OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) displays, known for their perfect black levels, infinite contrast ratios, and vibrant colors, are becoming increasingly popular in high-end televisions and smartphones.
MicroLED technology, which offers similar advantages to OLED with potentially even higher brightness and improved energy efficiency, is another promising development that could revolutionize display technology in the long term.
Q&A
Is 2K better than HD?
Yes, generally speaking, 2K resolution is considered better than standard HD (High Definition). Standard HD is typically 720p (1280×720 pixels). 2K most commonly refers to resolutions around 2000 pixels wide, often encompassing Full HD (1920×1080 pixels) in consumer contexts, or the slightly wider DCI 2K cinema standard (2048×1080 pixels). In either case, 2K offers more pixels than 720p HD, resulting in a sharper and more detailed image.
What is the difference between Full HD, 2K, and 4K?
The primary difference lies in the number of pixels, which determines image sharpness and detail. Full HD (FHD) has a resolution of 1920×1080 pixels. 2K is often used interchangeably with Full HD in consumer markets, though technically DCI 2K is slightly wider at 2048×1080 pixels. 4K, also known as Ultra HD (UHD), significantly increases the pixel count to 3840×2160 pixels. Essentially, 4K offers four times the pixels of Full HD/2K, providing much greater clarity and detail.
Which is better, 4K or Full HD?
Technically, 4K is better than Full HD because it offers four times the number of pixels (3840×2160 vs 1920×1080). This higher pixel density results in a significantly sharper, clearer, and more detailed picture, especially noticeable on larger screens or when viewed up close. However, “better” can depend on factors like screen size, viewing distance, available content, and budget. For smaller screens or viewing from further away, the difference might be less apparent, and Full HD remains a very capable resolution.
Should I go 4K or 2K?
The choice between 2K (QHD/1440p) and 4K (UHD/2160p) depends on your priorities and hardware. 2K is often considered the “sweet spot” for gaming, as it provides a significant visual upgrade over 1080p while being easier for most graphics cards to run at high frame rates. On the other hand, 4K offers unparalleled sharpness and detail, making it the superior choice for productivity, creative work like video editing, and media consumption, especially on larger screens (27-inch and above). If you have a high-end PC and prioritize maximum visual fidelity, go for 4K; for a balanced, high-performance gaming experience, 2K is an excellent choice.
Read Next