Screen resolution defines the clarity and detail of the image displayed on your screen.
It is measured by the number of pixels arranged horizontally and vertically. Higher resolution generally means a sharper, more detailed picture.
The importance of resolution varies significantly depending on how you use your display. For gaming, resolution impacts both visual fidelity and the performance demands on your hardware.
Video editors require high resolution to see fine details in their footage.
Even for general browsing and office work, higher resolution can lead to sharper text and more screen real estate.
What is QHD?
QHD stands for Quad High Definition.
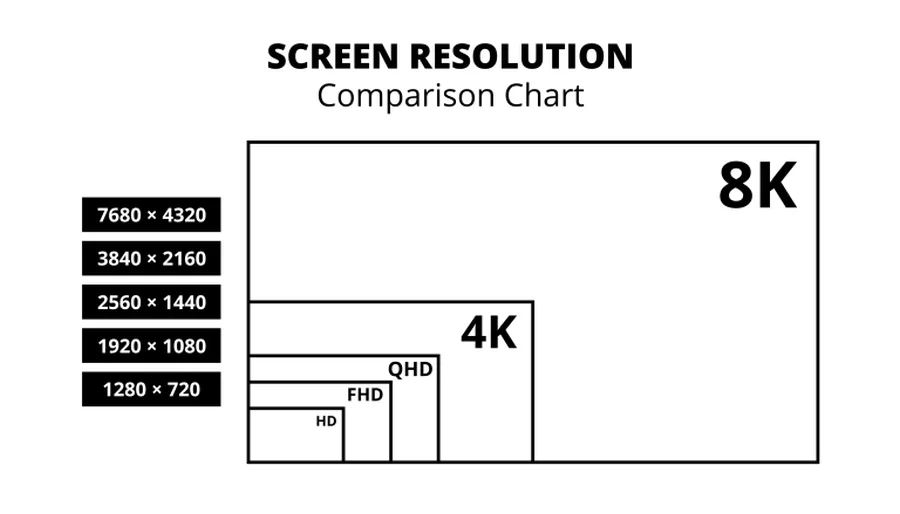
This resolution features 2560 pixels horizontally by 1440 pixels vertically (2560 x 1440). It offers four times the pixel count of standard HD (720p). QHD is the most common 2K resolution.
QHD is commonly found in computer monitors, particularly those aimed at gaming or productivity. Many modern high-performance laptops also utilize QHD displays.
Some premium smartphones have adopted QHD resolution for incredibly sharp visuals on smaller screens.
Advantages of QHD include:
- A significant visual improvement over Full HD (1080p), offering noticeably sharper images.
- Being less demanding on graphics cards compared to 4K, allowing for higher frame rates in games or smoother performance on less powerful hardware.
- Often available with high refresh rates (144Hz+) at more affordable price points than comparable 4K monitors.
Disadvantages of QHD include:
- It is not as pixel-dense or sharp as 4K resolution.
- QHD displays are typically more expensive than their Full HD counterparts.
What is 4K?
4K resolution is also commonly referred to as Ultra High Definition (UHD). It packs a dense 3840 pixels horizontally by 2160 pixels vertically.
This equates to four times the pixel count of Full HD (1080p) and significantly more than QHD.

4K has become the standard resolution for modern televisions.
It is also prevalent in high-end computer monitors, especially those designed for professional creative work like video editing and graphic design.
Current-generation gaming consoles, such as the PlayStation 5 and Xbox Series X, target 4K resolution for many games.
Advantages of 4K include:
- Exceptional visual clarity, sharpness, and detail, making images look incredibly lifelike.
- Being particularly beneficial on larger screen sizes, where the high pixel density maintains sharpness and prevents individual pixels from becoming obvious.
- Providing the best experience for viewing native 4K video content and high-resolution photographs.
Disadvantages of 4K include:
- Requiring substantially more powerful graphics hardware (GPU) to run demanding applications, especially games, at smooth frame rates.
- 4K monitors and televisions are generally more expensive than QHD options.
- On smaller screen sizes (e.g., under 27 inches), the visual benefit over QHD might be less apparent to some users.
QHD vs. 4K: Key Comparisons
| Feature | QHD (2560×1440) | 4K (3840×2160) |
|---|---|---|
| Pixel Count | ~3.7 million pixels | ~8.3 million pixels |
| Visual Clarity | Noticeably sharper than 1080p; Good detail. | Exceptionally sharp and detailed; Best image fidelity. |
| Pixel Density | High, but lower than 4K on same-sized screens. | Very high, leading to smoother images, especially on larger screens. |
| Performance Demands | Moderate GPU load; Easier to achieve high frame rates. | High GPU load; Requires powerful hardware for smooth gaming/rendering. |
| Hardware Requirements | Mid-range to high-end GPU recommended for gaming. | High-end GPU essential for demanding tasks, especially gaming. |
| Price | Generally more affordable than 4K displays. | Typically more expensive than QHD displays. |
| Ideal Use Cases | Gaming (balancing visuals & high refresh rates), general productivity, budget-conscious upgrade from 1080p. | Professional creative work (video/photo editing, design), premium movie viewing, ultimate visual fidelity (with powerful hardware). |
| Refresh Rate Availability | High refresh rates (144Hz+) more common and affordable. | High refresh rates often come at a significant price premium. |
Regarding visual clarity and sharpness, 4K boasts significantly more pixels than QHD.
This higher pixel count results in greater pixel density, leading to potentially sharper and more detailed images, especially noticeable on larger displays.
In terms of performance and hardware requirements, driving 4K resolution places a much heavier load on your system’s graphics card (GPU).
This means achieving high frame rates in demanding games or rendering complex projects is considerably more challenging at 4K than at QHD.
When comparing prices, QHD monitors and laptops typically come with a lower price tag than their 4K equivalents.
The best resolution ultimately depends on the specific use-case scenario.
Which Resolution Should You Choose?
You should opt for QHD if you are a gamer looking for a balance between strong visual quality and high refresh rates (like 144Hz or above).
QHD is also a great choice for users whose graphics hardware might struggle to consistently run games smoothly at 4K.
Budget-conscious users seeking a clear upgrade from Full HD without the significant cost jump and hardware demands of 4K will find QHD appealing.
You should go for 4K if you are a professional creative, such as a video editor, photographer, or graphic designer, who requires the maximum detail and screen real estate for your work.
Movie enthusiasts with access to native 4K content will benefit most from a 4K display’s clarity. Users with high-end hardware who prioritize the absolute sharpest image quality possible might also choose 4K.
Looking at future trends, resolutions beyond 4K, like 8K, are emerging but are still far from mainstream adoption.
Advancements in upscaling technologies (like NVIDIA DLSS or AMD FSR) are also becoming increasingly important, helping to achieve better performance at higher target resolutions.
Conclusion
In summary, QHD (1440p) provides a fantastic middle ground, offering a clear visual upgrade over 1080p without the extreme hardware demands of 4K.
4K (2160p) delivers superior sharpness and detail, making it ideal for specific professional tasks and premium media consumption, but it requires powerful hardware and costs more.
Your final decision should be based on a careful assessment of your primary use case, your budget, and the capabilities of your current or planned hardware.
Choose QHD for balanced performance, especially in gaming, or 4K for the ultimate visual fidelity in creative work and media viewing.
Q&A
Is there a noticeable difference between 1440p and 4K?
Yes, there’s generally a noticeable difference, particularly on larger monitors (27-inch+) or when viewed closely. 4K (3840×2160 pixels) offers significantly greater pixel density than 1440p (2560×1440 pixels), leading to sharper text, finer image details, and a crisper overall picture. The distinction might be less obvious on smaller screens or at greater viewing distances.
Is 2560×1600 resolution 4K?
No, 2560×1600 resolution is not 4K. It’s commonly known as WQXGA and has a 16:10 aspect ratio, offering more vertical space than standard QHD (1440p). While it provides more pixels than Full HD (1080p) and standard QHD (1440p), it falls considerably short of the 3840×2160 pixels required for 4K UHD resolution.
Is a 27-inch monitor QHD or 4K?
A 27-inch monitor can come in various resolutions, including QHD (2560×1440) and 4K (3840×2160), as well as Full HD (1080p). Screen size alone doesn’t dictate the resolution. QHD is often considered a ‘sweet spot’ for 27-inch displays, balancing clarity and performance demands, while 4K offers superior sharpness at this size. Always check the monitor’s specifications to confirm its native resolution.
What is better, 4K or UHD?
For consumer displays like TVs and monitors, ‘4K’ and ‘UHD’ (Ultra High Definition) are generally used interchangeably to describe the same resolution: 3840×2160 pixels. While a slightly different ‘DCI 4K’ (4096×2160) standard exists for professional cinema, when you see ‘4K’ or ‘UHD’ advertised for a consumer product, they almost always mean 3840×2160. Therefore, in this context, neither is ‘better’ – they refer to the same thing.
Is QHD better than 4K?
Whether QHD (Quad HD, 2560×1440) is ‘better’ than 4K (3840×2160) depends on your needs and hardware. 4K provides superior sharpness and detail due to its higher pixel density. However, QHD is significantly less demanding on your computer’s graphics card, making it easier to achieve high frame rates in gaming and generally requiring less powerful (and often less expensive) hardware. For many users, especially gamers prioritizing performance or those on a tighter budget, QHD offers a great balance.
Read Next













