High Dynamic Range, or HDR, represents a significant leap forward in display technology, moving beyond simply increasing pixel counts (like 4K resolution) to enhancing the quality of each pixel.
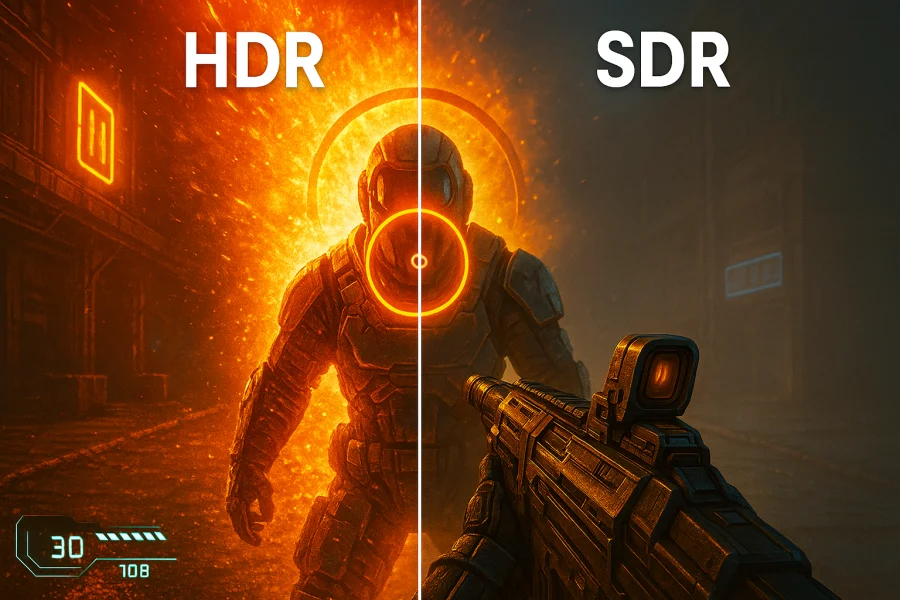
It expands the contrast ratio and color palette of an image, delivering brighter whites, deeper blacks, and a wider spectrum of colors that appear more lifelike compared to traditional Standard Dynamic Range (SDR).
Initially prominent in photography and television, HDR has rapidly found its footing in the video game industry. The rise of HDR gaming is driven by the desire for greater immersion.
For gamers, HDR isn’t just a minor upgrade; it fundamentally changes how virtual worlds are perceived, making HDR Gaming a crucial technology for anyone seeking the most realistic and engaging entertainment experience possible.
What is HDR Gaming?
At its core, HDR Gaming is a technology that enhances the visual experience in video games by improving contrast, brightness, and color accuracy.
Unlike SDR, which typically uses an 8-bit color depth and has a limited range of brightness (luminance, measured in nits), HDR utilizes 10-bit or even 12-bit color depth.
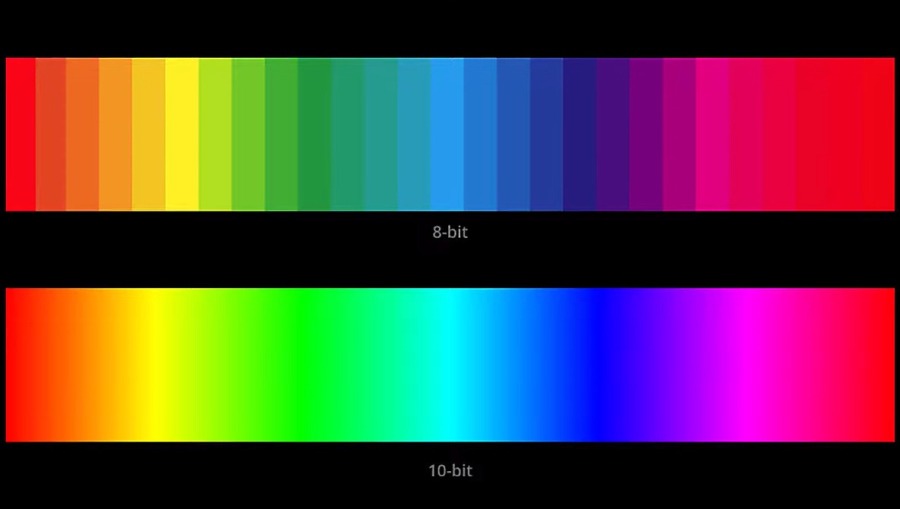

This allows for billions of colors instead of millions, resulting in smoother gradients and more nuanced shades.
Crucially, HDR significantly increases the peak brightness and lowers the black levels a display can achieve simultaneously.
This wider range allows game developers to render scenes with incredibly bright highlights (like sunlight glinting off metal, explosions, or magical effects) alongside deep, detailed shadows, all within the same frame, much closer to how we perceive light and color in the real world.

It’s about making the virtual world look less like a flat image on a screen and more like a window into a real space.
Benefits of HDR for Gamers
Implementing HDR correctly offers tangible advantages that significantly enhance the gaming experience.
Perhaps most importantly, it increases realism and immersion; by mimicking real-world light and shadow interplay, HDR makes game environments feel more convincing. Explosions pop with searing intensity, dark dungeons reveal subtle details without appearing washed out.
Another key benefit is improved detail visibility. The expanded dynamic range means you can discern more detail in both very bright and very dark areas simultaneously, which can even offer a competitive edge by revealing opponents lurking in shadows or details in bright skies that would be clipped in SDR.
Furthermore, HDR supports wider color gamuts (like DCI-P3 or Rec.2020), translating to more vibrant and accurate colors that better align with the developers’ artistic intent.
Finally, the enhanced contrast and color precision contribute to a greater sense of depth, making objects feel more solid and environments more expansive.
Hardware Requirements
To experience true HDR gaming, specific hardware is essential. The most critical component is an HDR-capable display – a TV or monitor explicitly supporting HDR.
Look for certifications like VESA DisplayHDR (e.g., DisplayHDR 400, 600, 1000, where higher numbers generally mean better peak brightness), Ultra HD Premium, or detailed manufacturer specs covering HDR format support (HDR10, Dolby Vision, etc.), peak brightness (aiming for 600-1000+ nits for impactful HDR, though 400 is a minimum), and good contrast/black levels (OLEDs excel here).
You also need a compatible source: on PC, this means modern graphics cards from NVIDIA (GeForce 10 series+) or AMD (Radeon RX 400 series+), while consoles like the PlayStation 4 Pro, PS5, Xbox One S/X, and Xbox Series S/X all support HDR output.
Lastly, ensure you’re using appropriate cables, typically High-Speed HDMI (HDMI 2.0a or ideally 2.1) or DisplayPort 1.4, capable of handling the required bandwidth for HDR signals.
Software and Game Support
Hardware readiness is only part of the equation; software and games must also support HDR.
Examples of games with excellent HDR implementation
Many modern AAA titles feature HDR support, though the quality of implementation can vary. Some standouts often praised for their HDR include:
- Cyberpunk 2077 (especially on PC with calibration)
- Red Dead Redemption 2
- Horizon Forbidden West / Horizon Zero Dawn
- Elden Ring
- Ori and the Will of the Wisps
- Gears 5
- Ratchet & Clank: Rift Apart
- Microsoft Flight Simulator
Game engines that support HDR
Major game engines have integrated HDR rendering pipelines, making it easier for developers to implement:
- Unreal Engine (versions 4 and 5)
- Unity
- Proprietary engines like Decima Engine (Guerrilla Games), RAGE Engine (Rockstar Games), REDengine (CD PROJEKT RED).
How HDR is implemented differently across titles
Not all HDR is created equal. Some games offer extensive calibration options (setting peak brightness, black point, paper white/mid-tones), allowing users to tailor the experience to their specific display.
Others might have minimal settings or rely heavily on AutoHDR features (like on Windows 11 or Xbox).
Some older or poorly implemented HDR modes might simply stretch the SDR signal, resulting in a washed-out or inaccurate image (“fake HDR”). The quality depends heavily on the developer’s effort and understanding of HDR principles.
Setting Up HDR for Gaming
Proper setup is crucial for getting the best HDR experience.
How to enable HDR on PC and console:
- Windows (10/11): Go to Settings > System > Display. Select your HDR-capable display, and toggle “Use HDR”. Further calibration might be needed via the “HDR” sub-menu or the Windows HDR Calibration app.
- PlayStation 5: Go to Settings > Screen and Video > Video Output. HDR is usually set to “On When Supported”. You can adjust HDR calibration settings here too.
- Xbox Series X/S: Go to Settings > General > TV & display options > Video modes. Ensure “Allow HDR10” (and potentially “Dolby Vision for Gaming” if supported) is checked. Calibration tools are available under “Calibrate HDR for games”.
Calibration tips for optimal performance:
- Use In-Game Calibration: Always prioritize the game’s specific HDR calibration settings if available. These often provide test patterns to set maximum brightness (until a pattern disappears), minimum brightness (black level), and sometimes a “paper white” setting for UI elements.
- Use OS Calibration Tools: Utilize the Windows HDR Calibration app or the console’s built-in HDR calibration process. This helps the system understand your display’s capabilities.
- Adjust Display Settings: Ensure HDR mode is enabled on your TV/monitor. Check settings like Black Level (often needs to be set to ‘Low’ or ‘Limited’ for HDMI sources, depending on console output), and disable any aggressive dynamic contrast or image processing that might interfere with the HDR signal.
Common setup pitfalls and how to avoid them:
- Incorrect Cable: Using an old HDMI cable that doesn’t support sufficient bandwidth. -> Use certified High-Speed or Ultra High-Speed HDMI cables.
- Display Setting Mismatch: HDR enabled in the OS/console but not on the display itself (or vice-versa). -> Check both device settings.
- Poor Calibration: Default settings often don’t match your specific display. -> Always calibrate.
- Windows SDR Content Brightness: The slider in Windows HDR settings affects how bright SDR content appears when HDR is active. Adjust this for comfortable viewing of non-HDR apps. -> Set it to a balanced level (often low).
- Conflicting Software: Some screen overlay software or capture tools can interfere with HDR. -> Disable them if experiencing issues.
HDR Formats Explained
Several HDR formats exist. HDR10 is the most common open standard, using static metadata (brightness/color info set once for the whole content) and requiring a 10-bit display. It offers the widest compatibility but is less precise than dynamic formats.
Dolby Vision, a proprietary format, uses dynamic metadata, adjusting visuals scene-by-scene or frame-by-frame for potentially superior optimization, but requires licenses and specific support.
HLG (Hybrid Log-Gamma) is primarily for broadcast TV, offering backward compatibility with SDR but rarely used in gaming.
HDR10+ is an open-standard alternative to Dolby Vision, also using dynamic metadata, but its adoption in gaming currently lags behind HDR10 and Dolby Vision.
Regarding platform compatibility: PCs primarily support HDR10, with conditional support for Dolby Vision/HDR10+ depending on hardware and software.
Xbox consoles support HDR10 and Dolby Vision for Gaming (with a compatible TV). PlayStation consoles support HDR10 for gaming but not Dolby Vision (though they do supports it for streaming apps/Blu-ray)..
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its benefits, HDR in gaming faces hurdles. The quality of implementation is inconsistent across games, with some looking worse than well-mastered SDR.
Achieving optimal results demands careful calibration specific to the display and game, which can be complex for users.
High-quality HDR displays remain relatively expensive compared to SDR counterparts. Operating systems like Windows can still exhibit quirks when handling HDR, especially with mixed SDR/HDR content.
Furthermore, the “HDR compatible” label on lower-end displays doesn’t guarantee a significant improvement, as limited peak brightness or poor local dimming can restrict the impact.
The Future of HDR Gaming
The trajectory for HDR gaming is positive. We anticipate wider adoption of dynamic metadata formats like Dolby Vision and HDR10+ for more refined visuals.
Standardization efforts should simplify setup and calibration, perhaps through improved OS-level tools. Game engines will likely feature deeper and more sophisticated HDR integration as standard.
Display technology continues to advance (MicroLED, better OLEDs, higher brightness, improved dimming), making high-quality HDR more accessible.
Finally, technologies like Microsoft’s AutoHDR, which intelligently adds HDR effects to SDR games, are expected to become more refined and widespread.
Q&A
Should HDR be on or off gaming?
Generally, HDR should be turned on if you have a compatible HDR display (TV or monitor) and your console or PC supports it. It can drastically improve visual fidelity. However, turn it off if your display isn’t HDR-capable, if a specific game’s HDR implementation looks poor (e.g., washed out or too dark), or sometimes for competitive gaming where maximum visibility in shadows might be prioritized over visual richness.
Do games look better in HDR?
Yes, when implemented well and viewed on a capable HDR display, games typically look significantly better in HDR. The enhanced contrast reveals more detail in both very bright and very dark areas of the screen, while the wider color gamut makes visuals appear richer and more lifelike. However, the quality of HDR can vary between games.
What is HDR mode in games?
HDR mode is usually a specific setting found within a game’s video or display options menu. Enabling this mode tells the game to output an HDR signal, utilizing the extended brightness and color capabilities of your compatible hardware (display, console/PC, and cable). Often, activating this mode also prompts in-game calibration steps to match the HDR output to your specific display’s performance.
Read Next













