Navigating the world of modern display technology can feel like wading through alphabet soup – LED, QLED, HDR, OLED, 4K, 8K.
Among the most frequently discussed and often confused terms are HDR and OLED.
You’ll often see them mentioned together when discussing high-end TVs or monitors, leading many to wonder if they’re competing technologies or different aspects of the same thing.
The truth is, they aren’t directly comparable in the way you might think. This article will demystify HDR and OLED, explain their individual roles, and clarify how they relate to each other to help you understand what truly matters for your viewing experience.
What Is HDR?
HDR stands for High Dynamic Range. Unlike terms that describe the physical panel of a display (like OLED or LCD), HDR refers to the image signal and how a compatible display interprets it.
Think of it as an enhancement to the picture information itself. Standard Dynamic Range (SDR), which was the norm for decades, has limitations in the range of brightness (luminance) and color (gamut) it can represent. HDR significantly expands this range.
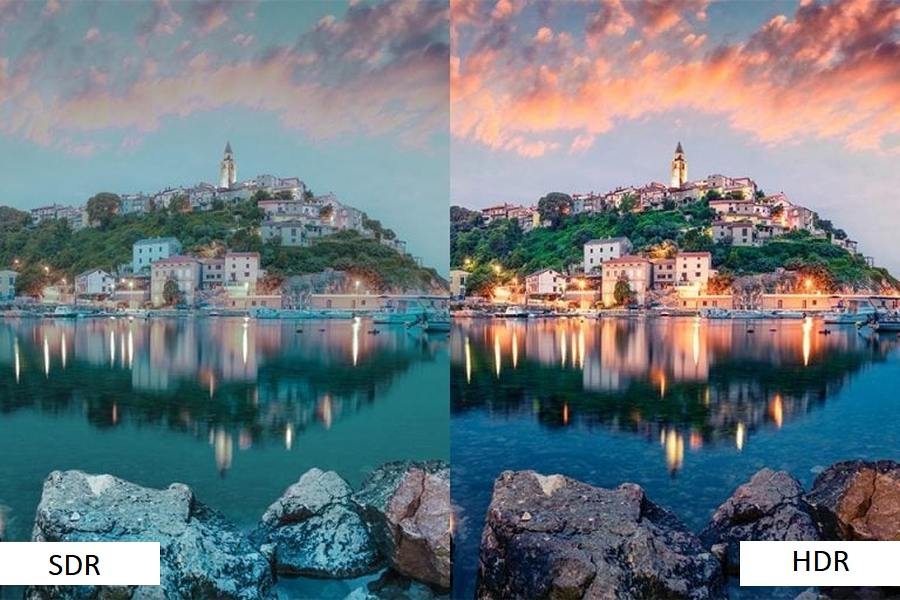

For the viewer, this translates into several key improvements. HDR allows for much brighter peak highlights, making elements like the glint of sunlight on water, reflections, or explosions appear far more intense and realistic.
Simultaneously, while making highlights brighter, HDR also enables the preservation of more detail within the darkest parts of an image, preventing them from looking like flat, indistinct shadows.
Furthermore, HDR typically accompanies specifications for displaying a wider color gamut, resulting in richer, more vibrant, and lifelike hues compared to traditional SDR content.
Crucially, HDR is a format and capability requiring both ends of the chain.
You need HDR-encoded content, such as specific streams on platforms like Netflix, UHD Blu-rays, or modern video games, and you also need a display capable of processing and showing that HDR signal – an “HDR-compatible” TV or monitor – to experience the benefits.
Common HDR formats include HDR10, HDR10+, Dolby Vision, and HLG.
What Is OLED?
OLED stands for Organic Light Emitting Diode. This is a type of display panel technology, fundamentally different from the more common LCD/LED panels.
In a traditional LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) panel, an LED backlight shines through layers of liquid crystals and color filters to generate an image.
Even when attempting to display black, this backlight is usually active to some degree, leading to imperfect blacks, sometimes referred to as “gray,” and potential light bleed around bright objects.
OLED technology operates on a distinct principle. Each individual pixel within an OLED display is composed of an organic compound that emits its own light when electricity is applied.
This self-emissive nature provides several unique characteristics. Most notably, it allows for perfect blacks, as any pixel needing to be black can simply turn off completely, creating an effectively infinite contrast ratio – the difference between the brightest white and the darkest black.
This self-lighting capability also contributes to highly saturated and vibrant colors. Additionally, OLED panels offer wide viewing angles, meaning colors and contrast remain consistent even when viewing the screen from off-center positions.
Their pixels can also switch on and off almost instantaneously, resulting in fast response times that minimize motion blur, making them excellent for fast-moving content like sports and gaming.
OLED technology is generally found in premium TVs and some high-end monitors and smartphones.
HDR vs OLED: Head-to-Head Comparison
| Feature | HDR (Tech/Standard) | OLED (Display Tech) |
|---|---|---|
| Brightness | Very high (esp. HDR10+) | Moderate (but punchy due to contrast) |
| Black Levels | Depends on display tech | Perfect blacks |
| Contrast | Enhanced via signal | Native due to pixel control |
| Color Range | Wide color gamut | Naturally wide due to OLED tech |
| Viewing Angles | Depends on panel | Excellent |
| Power Efficiency | Varies | Less efficient at high brightness |
| Cost | Affordable on LED TVs | Premium price point |
This is where the core confusion often arises, as we’re comparing an image enhancement standard (HDR) with a panel technology (OLED). They aren’t mutually exclusive; in fact, they frequently work together to deliver a superior picture.
The fundamental difference lies in their roles: HDR concerns the range of light and color contained within the video signal itself, while OLED describes how the screen physically creates the image using self-illuminating pixels.
Regarding compatibility, an OLED display can be, and in the TV market almost universally is, HDR-compatible. Its inherent ability to produce perfect blacks and control light at the individual pixel level makes it exceptionally well-suited for rendering the nuances of HDR content.
OLED technology offers infinite contrast due to its ability to achieve true black. HDR content leverages the contrast capabilities of whatever display it’s shown on. On an OLED panel, HDR looks incredibly dynamic precisely because of this inherent contrast advantage.
While high-quality LCDs use sophisticated local dimming to enhance contrast for HDR, they cannot match the per-pixel precision of OLED.
Conversely, when it comes to brightness, high-end LCD/LED technologies like QLED and Mini-LED often surpass OLED in sheer peak luminance, which can be beneficial for impactful HDR highlights, especially in brighter rooms.
OLED brightness capabilities, however, continue to improve with each generation.
HDR vs OLED Use Cases: Which One Is Right for You?
Since the choice isn’t typically “HDR or OLED” in isolation – given that modern OLED TVs support HDR, and many non-OLED TVs also offer HDR – the practical decision revolves around prioritizing panel technology based on your viewing habits and environment, while considering HDR support a vital feature regardless of panel type.
Movies and television
For dedicated movie lovers, especially those who enjoy watching in darkened environments, OLED often emerges as the top choice.
Its perfect black levels and pixel-level light control create unparalleled contrast, making cinematic content incredibly immersive. HDR movies and television shows truly excel on OLED displays, showcasing deep shadows and detailed highlights simultaneously.
Bright Room Viewing
If your television will primarily reside in a very bright, sunlit room, a high-brightness QLED or Mini-LED TV featuring excellent HDR performance might be a more suitable option.
The capacity of these displays to achieve significantly higher peak brightness levels can effectively counteract ambient light, ensuring HDR highlights remain impactful and visible even during daytime viewing.
For Gamers
Gamers find compelling options in both camps. OLED panels offer near-instantaneous response times and perfect blacks, maintaining clarity during fast-paced gameplay, making dark scenes particularly effective.
High-end LCDs, on the other hand, might provide higher peak brightness for more dazzling HDR effects in games and potentially offer higher refresh rates in certain models.
Key factors for gamers on either technology include low input lag and support for features like Variable Refresh Rate (VRR), alongside strong HDR implementation.
Budget-Conscious Buyers
For budget-conscious buyers, OLED technology generally remains in the premium price tier. HDR support, however, has become more widespread and is available across a broader range of price points, including numerous mid-range and even some budget-friendly LCD/LED televisions.
It is crucial to understand that the quality and impact of the HDR experience will vary significantly depending on the underlying panel’s capabilities (like peak brightness and local dimming performance), but basic HDR compatibility can be obtained without investing in OLED.
Conclusion
HDR and OLED are not competing entities but rather distinct components contributing to the modern viewing experience.
HDR is an enhancement to the video signal, offering greater brightness, deeper contrast, and more vibrant colors. OLED is a sophisticated display panel technology known for its perfect blacks, infinite contrast, and pixel-level control.
While often found together in high-end TVs, where OLED panels provide an ideal canvas for HDR content, they serve different functions.
Understanding this distinction is key: HDR defines what information is in the picture, while OLED defines how that picture is physically created on screen.
Choosing the right display involves considering how well a particular panel technology, whether OLED or a type of advanced LCD, can realize the potential of HDR content within your specific viewing environment and budget.
Q&A
Is 4K HDR better than OLED?
This compares apples and oranges. 4K refers to screen resolution (pixel count), while HDR (High Dynamic Range) relates to contrast and color depth. OLED is a specific display panel technology known for its perfect blacks and pixel-level control. You can, and often do, have OLED TVs that are also 4K and support HDR. The best viewing experience often combines these: a 4K OLED TV with HDR capabilities delivers both sharp detail and stunning contrast/color.
Which is better, HDR or OLED or QLED?
Again, HDR isn’t directly comparable to OLED or QLED, as it’s a picture enhancement feature that both types of TVs can support. When comparing OLED and QLED (a type of advanced LED-backlit LCD TV), OLED excels at perfect black levels and infinite contrast, ideal for dark rooms. QLED typically offers higher peak brightness, vibrant colors, and isn’t susceptible to burn-in, making it great for bright rooms. Both technologies deliver fantastic picture quality when paired with HDR content, so the “better” choice depends on your viewing environment and priorities.
Is OLED still the best picture quality?
OLED is still widely considered among the best for overall picture quality, primarily due to its ability to produce perfect blacks and infinite contrast ratios. This leads to incredible depth and detail, especially in darker scenes. However, technologies like high-end QLED and Mini-LED TVs offer strong competition, particularly in terms of peak brightness and performance in very bright rooms. While OLED remains a top contender, especially for cinephiles, the “best” can be subjective and depend on specific viewing conditions.
What is the difference between OLED and HDR LED?
OLED (Organic Light Emitting Diode) is a display technology where each pixel creates its own light and can be turned off completely, resulting in perfect blacks and infinite contrast. “HDR LED” typically refers to an LED-backlit LCD TV that supports HDR content. The core difference is the light source: OLED pixels are self-lit, while LED TVs use an LED backlight (either edge-lit or full-array) shining through an LCD panel to create the image. This fundamental difference means OLED generally offers superior contrast and viewing angles, while LED TVs can achieve higher peak brightness and are immune to potential burn-in.
Read Next













