Display technology has come a long way since the early days of cathode ray tubes.
In recent years, OLED (Organic Light-Emitting Diode) has emerged as a game-changer in the world of displays. OLED technology has revolutionized screens in smartphones, TVs, and other devices with its vibrant colors and deep blacks.
Recently, a new variant called PHOLED (Phosphorescent OLED) has emerged, promising even greater efficiency and performance.
Understanding the differences and advantages between OLED and PHOLED is crucial for consumers and industry professionals alike.
What is OLED?
OLED, or Organic Light-Emitting Diode, is a type of display technology that uses organic compounds to emit light when an electric current is applied.
Each pixel in an OLED display is composed of organic molecules that generate their own light, eliminating the need for a backlight.
This allows OLED displays to achieve perfect blacks and infinite contrast ratios, as pixels can be completely turned off.
The working principle of OLED involves several layers, including an emissive layer made of organic compounds sandwiched between two electrodes.
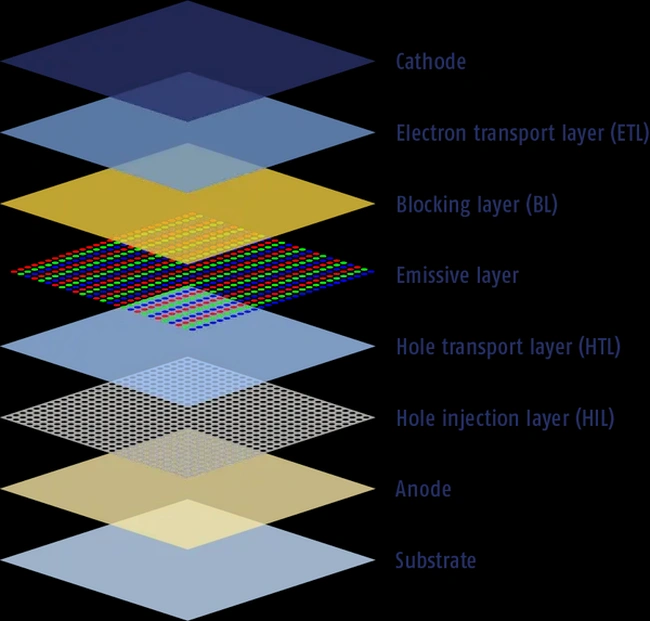
When electricity is applied, electrons and holes combine in the emissive layer, causing the organic material to emit light.
This process allows OLEDs to produce vibrant colors and high contrast images.
The advantages of OLED technology are numerous.
First, OLED displays can achieve perfect blacks and high contrast ratios, making them ideal for high-quality video and gaming experiences.
OLEDs also offer wider viewing angles and faster response times compared to conventional LCDs, reducing motion blur and providing a smoother visual experience.
Additionally, OLED panels can be made flexible and thin, enabling innovative designs such as curved and foldable screens.
What is PHOLED?
PHOLED, or Phosphorescent OLED, is an advanced type of OLED technology that uses phosphorescent materials to achieve higher efficiency.
Unlike traditional OLEDs, which use fluorescent materials, PHOLEDs incorporate materials that can harvest both singlet and triplet excitons (bound pairs of electrons and holes) for light emission.
This results in nearly 100% internal quantum efficiency compared to the 25% efficiency typically seen in fluorescent OLEDs.
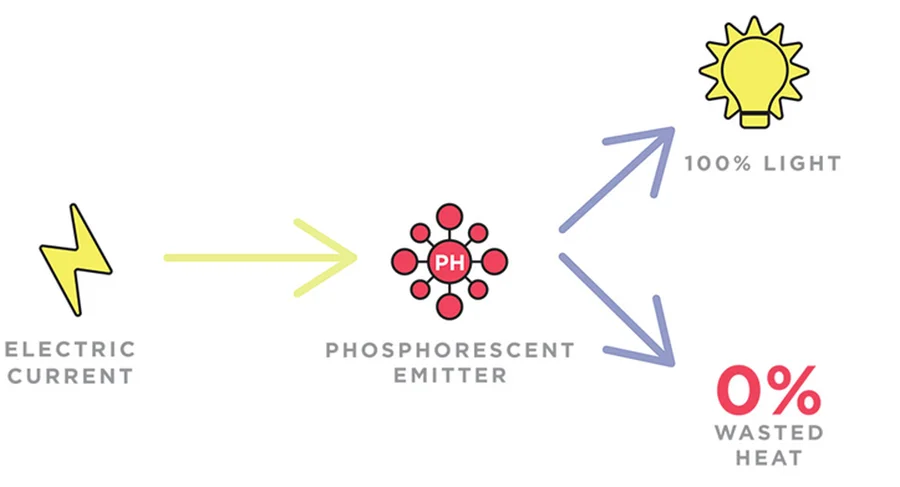
The working mechanism of PHOLED is similar to that of traditional OLED, with a crucial difference in the emissive layer.
In PHOLEDs, phosphorescent compounds are used in the emissive layer, allowing them to emit light for a longer duration.
This leads to more efficient light production, as more energy is converted into visible light rather than being wasted as heat.
The key differences between PHOLED and traditional OLED lie in their materials and efficiency.
PHOLEDs can produce more light with less electrical power, resulting in higher energy efficiency.
This means PHOLED displays can be brighter and consume less power than their OLED counterparts.
However, achieving stable blue PHOLEDs remains a challenge, since high energy required for blue light emission tends to degrade organic materials more quickly than red or green phosphorescent emitters.
Differences Between PHOLED and OLED
Energy Efficiency
PHOLED technology boasts significantly higher energy efficiency compared to traditional OLEDs.
By utilizing phosphorescent materials, PHOLEDs can achieve nearly 100% internal quantum efficiency.
This means more electrical energy is converted into light, resulting in less power consumption for the same level of brightness.
Brightness and Heat
PHOLEDs can produce more light with less heat generation due to their higher efficiency.
This allows PHOLED displays to achieve higher brightness levels without the risk of overheating.
As a result, PHOLED panels can deliver better performance in high ambient light conditions and extend the lifespan of the display.
Color Accuracy and Stability
One of the challenges in PHOLED technology is achieving stable and efficient blue phosphorescent materials.
While red and green PHOLEDs have demonstrated excellent performance, blue PHOLEDs still face issues with lifespan and efficiency.
This challenge affects overall color accuracy and the longevity of the display.
However, ongoing research aims to develop more stable blue PHOLED materials, which could lead to significant advancements in the technology .
Lifespan
PHOLED technology has the potential to improve the lifespan of displays due to its higher efficiency and lower operating temperatures.
Reducing heat generation not only enhances energy efficiency but also mitigates degradation of the organic materials, potentially leading to longer-lasting displays.
Current Applications and Future Prospects
OLED technology is currently widespread in various devices, including smartphones, TVs, monitors, and wearables.
High-end smartphones, such as those from Apple and Samsung, often feature OLED displays for their superior image quality and thin design.
OLED TVs have gained popularity in the home entertainment market, offering superior picture quality and thin form factors.
In the realm of monitors, OLED displays are favored by professionals who require precise color accuracy and fast response times.
Red and green PHOLEDs, for red and green pixels are already being used in commercial products such as TVs and smartphones.
These PHOLED materials contribute to the higher energy efficiency and improved brightness of these devices.
However, the development of stable and efficient blue PHOLEDs remains a challenge that researchers are actively working to overcome.
The future prospects for PHOLED are promising, with potential advancements in blue PHOLED materials leading to even more efficient and high-performance displays.
As these developments materialize, we can expect broader adoption of PHOLED technology in consumer electronics and new applications in fields requiring high efficiency and durability, such as automotive and aerospace displays.
Conclusion
In summary, OLED and PHOLED technologies represent significant advancements in display technology, each with its unique benefits and challenges.
OLEDs are renowned for their perfect blacks, high contrast ratios, and fast response times, making them ideal for various consumer electronics.
PHOLEDs, on the other hand, offer higher energy efficiency and the potential for greater brightness with less heat generation, positioning them as a promising evolution of OLED technology.
The potential impact of PHOLED on the display industry is substantial.
With ongoing research focused on improving blue PHOLED materials, the future holds the promise of even more efficient and long-lasting displays.
As PHOLED technology matures, we can anticipate its broader adoption across multiple industries, paving the way for innovative applications and enhanced user experiences.
The future of display technology looks bright with PHOLED, as it promises to build on the strengths of OLED while addressing its limitations.
Consumers and industry professionals alike should keep an eye on this evolving technology, as it has the potential to redefine the standards of visual excellence.
Q&A
What is a PHOLED TV?
PHOLED stands for Phosphorescent Organic Light Emitting Diode. It’s an advancement in OLED technology where phosphorescent materials are used for the light-emitting layers. Unlike traditional fluorescent OLED materials which have theoretical efficiency limits, phosphorescent materials can convert nearly 100% of electrical energy into light. This allows PHOLED displays to potentially achieve higher brightness, greater energy efficiency, and longer lifespans compared to earlier OLED types. Most modern high-performance OLED TVs already incorporate phosphorescent emitters, especially for red and green pixels.
Is p-OLED better than OLED?
“p-OLED” typically refers to Plastic OLED, which uses a flexible plastic substrate instead of the traditional rigid glass substrate found in most OLED TVs. This makes p-OLED displays thinner, lighter, and bendable, which is why they’re commonly used in smartphones, smartwatches, and foldable devices. It’s not inherently “better” than the glass-substrate OLED (often just called OLED) used in TVs; it’s different and suited for different applications. For large, flat-screen TVs, the rigidity and established manufacturing of glass OLED are often preferred, while p-OLED excels where flexibility or thinness is paramount.
Is there a better screen than OLED?
Whether a screen technology is “better” than OLED depends on your priorities. OLED is renowned for its perfect black levels, infinite contrast ratio, and wide viewing angles. However, high-end LED/LCD technologies like QLED and Mini-LED can achieve significantly higher peak brightness, making them excellent choices for very bright rooms, and they have no risk of burn-in. Emerging technologies like MicroLED promise the benefits of OLED (perfect blacks) with even higher brightness and longer lifespan, but are currently extremely expensive. QD-OLED is another variant aiming to improve brightness and color volume over traditional OLEDs. Ultimately, the “best” screen depends on your viewing environment, budget, and what picture quality aspects matter most to you.
Read Next