Modern electronic devices constantly push the boundaries of screen quality. Users demand vibrant colours, deep blacks, and smooth motion.
Simultaneously, expectations for long battery life have never been higher. Reconciling high-performance displays with power efficiency is a major challenge for manufacturers.
LTPO display technology has emerged as a crucial innovation in addressing this very challenge. This technology allows screens to operate more intelligently, adapting to the content being viewed.
We will explore what LTPO is, how it works, and the benefits it brings to our gadgets.
Understanding LTPO AMOLED Technology
LTPO (Low-Temperature Polycrystalline Oxide) is a type of backplane technology developed by Apple used primarily in OLED (specifically, AMOLED) displays.
The backplane is the layer behind the pixels that contains the thin-film transistors (TFTs) responsible for switching individual pixels on and off.
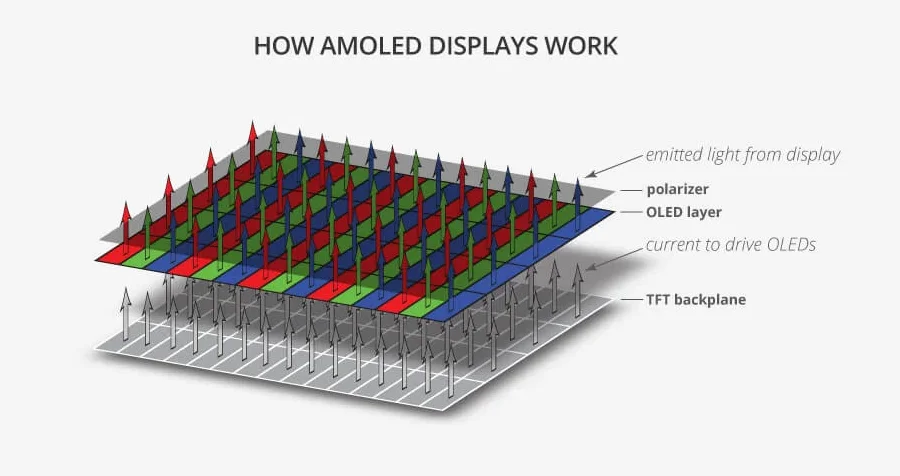
Traditional high-performance OLEDs often use LTPS (Low-Temperature Polycrystalline Silicon) for their backplanes, which allows for high electron mobility and thus high refresh rates.
LTPO technology innovatively combines the strengths of two different transistor types within the same backplane.
It integrates high-performance LTPS TFTs with power-efficient Oxide TFTs, which are often based on IGZO (Indium Gallium Zinc Oxide).
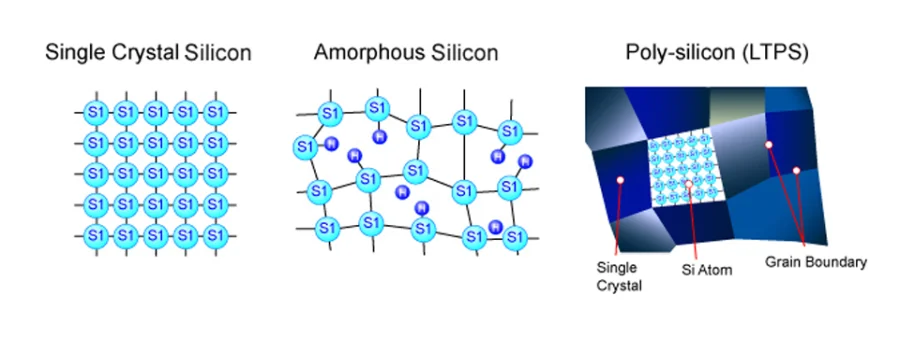
In simpler terms, LTPO displays combine the benefits of both LTPS and IGZO backplanes.
LTPS transistors are adept at the rapid pixel switching needed for high refresh rates. Their primary disadvantage, however, is relatively high leakage current. Essentially, even when turned ‘off’, these transistors still allow some current to leak through.
This becomes problematic for battery life when displaying static or slow-moving images, as this continuous leakage wastes power unnecessarily. When pixels don’t need constant updates, the energy lost through LTPS leakage counteracts the potential power savings from using a lower refresh rate.
Oxide TFTs have significantly lower leakage current, making them exceptionally efficient at holding a pixel’s state for static or slow-changing images. The Oxide transistor can also be used to ensure that the paired LTPS transistor is completely switched off, reducing wasteful leakage.
However, Oxide TFTs have some disadvantages; their uniformity of electron mobility is typically lower than that of LTPS, which can impact performance at very high refresh rates.
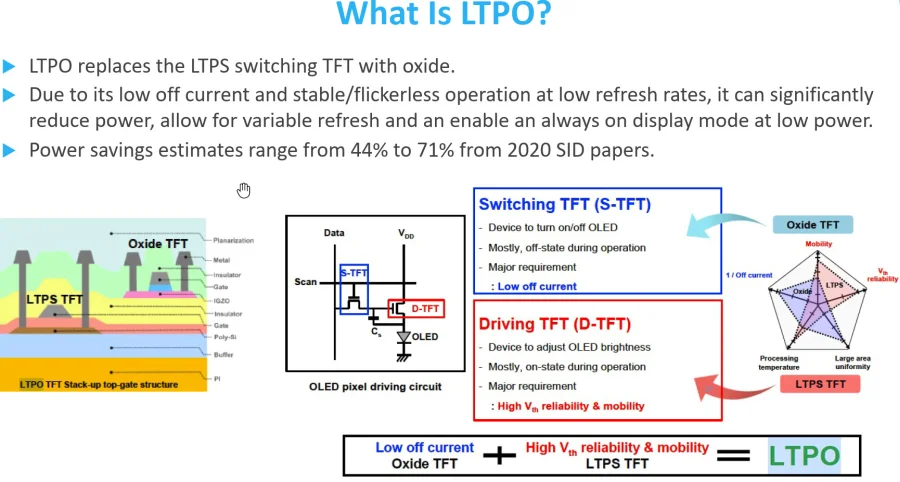
Therefore, this hybrid construction of both LTPS and Oxide TFTs is the key that enables a display’s refresh rate to vary dynamically over a wide range.
The refresh rate can intelligently drop to extremely low levels, such as 1Hz (once per second), when viewing static content like text or a photo.
Conversely, it can ramp up instantly to high levels, like 120Hz or more, for fluid motion during gaming or scrolling.
Advantages of LTPO Displays
The most significant advantage of LTPO technology is its impact on power consumption.
By drastically reducing the refresh rate when high speeds are unnecessary, LTPO displays save considerable amounts of energy.
This translates directly into longer battery life for the device.
It makes features like sophisticated always-on displays much more practical, showing information continuously without severely impacting battery endurance.
Users benefit from the best of both worlds: ultra-smooth motion when needed and optimised power saving when the content is static.
The variable refresh rate (VRR) capability enhances the perceived smoothness of interactions.
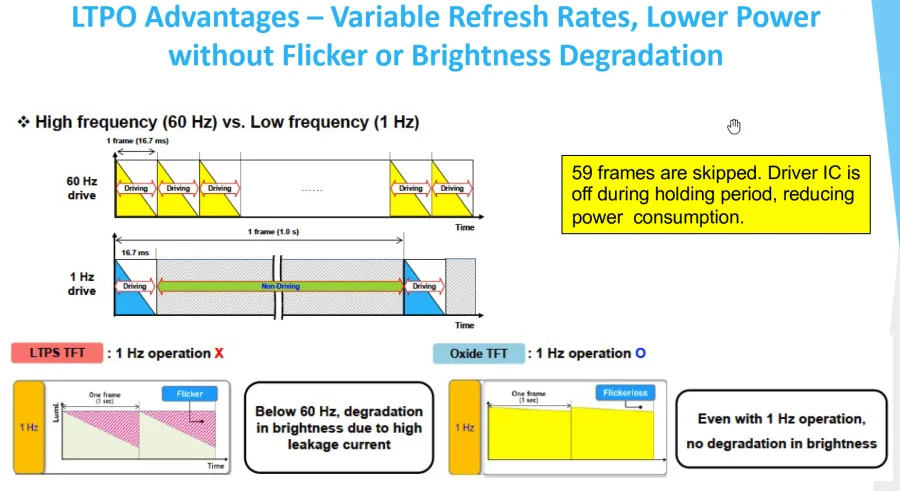
LTPO achieves this adaptability without compromising other aspects of image quality like color accuracy or brightness.
Key advantages include:
- Dynamic Refresh Rate: Ability to adjust refresh rates across a wide spectrum (e.g., 1Hz to 120Hz+).
- Power Efficiency: Significant reduction in display power draw, especially with static images.
- Improved Battery Life: Devices equipped with LTPO screens generally last longer on a single charge.
- Enhanced Always-On Displays: Enables more functional always-on features with lower battery penalty.
- Smoother Visuals: Seamless adaptation provides fluid motion without unnecessary power use.
LTPO vs. Other Display Technologies
Standard OLED (AMOLED) displays predominantly use LTPS backplanes.
While LTPS enables high refresh rates (like 120Hz), it is less efficient at maintaining very low refresh rates needed for optimal power saving with static content.
Such displays often operate at fixed rates (e.g., 60Hz or 120Hz) or switch between a limited number of predefined steps, lacking LTPO’s granular adaptability.
LTPO’s wide dynamic range (e.g., 1Hz-120Hz) offers superior power management compared to LTPS-only solutions.
Compared to traditional LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) technology, OLEDs (including those using LTPO) generally offer better contrast, true blacks, and often lower power consumption, especially when displaying dark content.
While LCD technology has adaptive sync features like FreeSync or G-Sync in a higher range (e.g., 40Hz up to 144Hz or more), LTPO specifically refers to the OLED backplane technology enabling VRR with exceptional power efficiency at the low refresh rates.
Basic Oxide TFT backplanes offer good power efficiency for static images but may lack the high performance of LTPS needed for smoothly driving pixels at very high refresh rates.
LTPO effectively combines the best attributes of both LTPS and Oxide TFTs.
Applications
LTPO technology first gained prominence and is now widely used in premium smartphones.
Flagship phones from major manufacturers often highlight LTPO as a key feature enabling both high refresh rates and better battery life.
Smartwatches are another critical application area for LTPO.

The technology’s power-saving capabilities are invaluable for extending the battery life of these small devices, especially those featuring always-on watch faces.
We are beginning to see LTPO explored for use in high-end tablets.
Potentially, laptops could also benefit in the future, particularly thin-and-light models where battery longevity is paramount.
Essentially, any battery-powered device with a display that benefits from both smooth motion and energy efficiency is a candidate for LTPO adoption.
Conclusion
LTPO display technology marks a significant milestone in the evolution of mobile screens. Its core capability – dynamically adjusting the refresh rate based on content – provides clear, tangible benefits.
Users gain a smoother visual experience during interaction and motion, coupled with noticeably improved battery performance. Features like effective always-on displays become more viable thanks to LTPO’s power-saving nature.
As the technology matures and potentially becomes more affordable to implement, LTPO is poised to become an increasingly standard feature across a wide range of personal electronics.
It represents a clever engineering solution balancing the demands for high fidelity and extended usage in modern devices.
Q&A
Is LTPO better than OLED?
It’s not really a case of LTPO versus OLED. LTPO (Low-Temperature Polycrystalline Oxide) is a type of backplane technology used to control the pixels in an OLED display. Think of it as an enhancement for OLED screens, allowing them to operate more efficiently, rather than a competing display type.
What is the benefit of LTPO?
The primary benefit of LTPO technology is significantly improved power efficiency. It allows the display’s refresh rate to dynamically adjust over a wide range (e.g., from as low as 1Hz to as high as 120Hz or more). This means the screen uses less power when displaying static content (like text or photos) and ramps up for smooth motion when needed (like scrolling or gaming).
What is Samsung LTPO?
Samsung LTPO refers to the LTPO display technology developed and manufactured by Samsung Display, a major producer of OLED panels. They often use specific branding for their LTPO implementations (like HOP – Hybrid Oxide and Polycrystalline silicon). Essentially, it’s Samsung’s version of the power-saving variable refresh rate technology for OLED screens used in many high-end smartphones and watches.
What is 120Hz LTPO?
A 120Hz LTPO display is an OLED screen capable of reaching a maximum refresh rate of 120Hz for ultra-smooth motion, but which also uses LTPO technology. This means it doesn’t always run at 120Hz; the LTPO backplane allows it to dynamically lower the refresh rate (sometimes down to 1Hz) when high speeds aren’t necessary, conserving battery life while still offering peak fluidity when required.
Is LTPO AMOLED better than OLED?
LTPO enhances AMOLED (a type of OLED). So, an LTPO AMOLED display offers advantages over a standard AMOLED display that uses older backplane technology (like LTPS) without variable refresh rate capabilities. The core pixel technology (AMOLED) provides the vibrant colours and deep blacks, while the LTPO backplane adds significant power savings, making LTPO AMOLED arguably “better” in terms of overall efficiency.
Is LTPO AMOLED good for eyes?
LTPO AMOLED displays generally share the characteristics of regular AMOLED screens regarding eye comfort, such as high contrast ratios and true blacks which can reduce strain in dark environments. The main benefit of LTPO itself is power saving, not directly eye comfort. However, the ability to run at high refresh rates (like 120Hz) can result in smoother motion, which some users find more comfortable and less fatiguing than lower, fixed refresh rates. Factors like brightness control (PWM dimming) still apply as they do to most OLEDs.
What is the difference between LTPO2 and LTPO3?
LTPO3 typically offers faster and smoother switching between refresh rates, potentially a wider dynamic range (reliably hitting 1Hz more often), and even greater power efficiency compared to LTPO2. Essentially, LTPO3 represents further optimization for saving battery life while maintaining a fluid visual experience.
Read Next













